|
Publication
Title
Regulation of arachidonic acid release and cytosolic phospholipase A2activation.
Authors
Gijon MA, Leslie CC.
Affiliation
Department of Pediatrics, National Jewish Medical and Research Center, Denver,Colorado 80206, USA.
Abstract
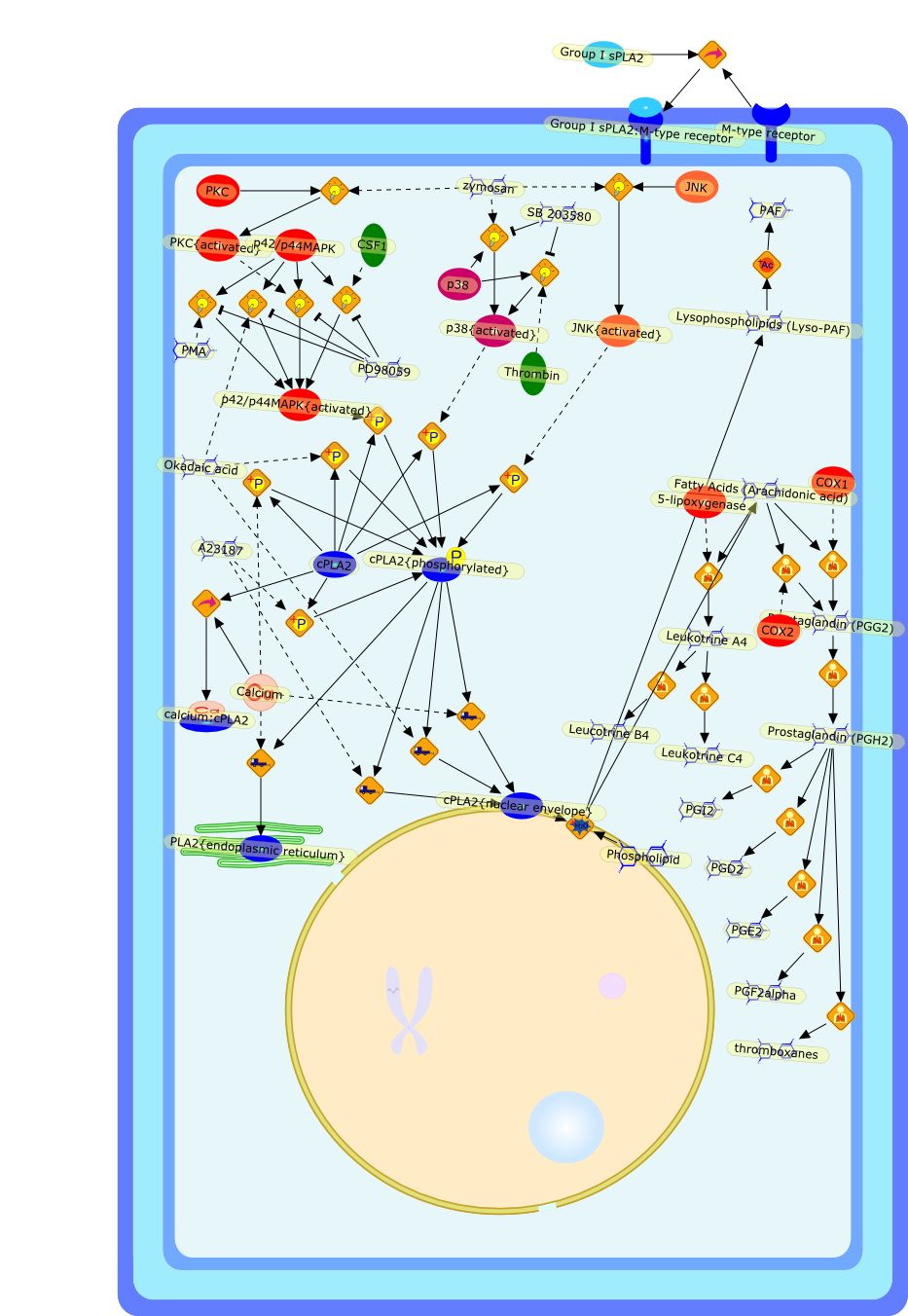
The 85-kDa cytosolic PLA2 (cPLA2) mediates agonist-induced arachidonic acidrelease in many cell models, including mouse peritoneal macrophages. cPLA2 isregulated by an increase in intracellular calcium, which binds to anamino-terminal C2 domain and induces its translocation to the nuclear envelopeand endoplasmic reticulum. Phosphorylation of cPLA2 on S505 by mitogen-activatedprotein kinases (MAPK) also contributes to activation. In macrophages, zymosaninduces a transient increase in intracellular calcium and activation of MAPK,which together fully activate cPLA2 and synergistically promote arachidonic acidrelease. There are alternative pathways for regulating cPLA2 in macrophagesbecause PMA and okadaic acid induce arachidonic acid release without increasingcalcium. The baculovirus expression system is a useful model to study cPLA2activation. Sf9 cells expressing cPLA2 release arachidonic acid to either A23187or okadaic acid. cPLA2 is phosphorylated on multiple sites in Sf9 cells, andphosphorylation of S727 is preferentially induced by okadaic acid. However, thephosphorylation sites are non-essential and only S505 phosphorylation partiallycontributes to cPLA2 activation in this model. Although okadaic acid does notincrease intracellular calcium in Sf9 cells, calcium binding by the C2 domain isnecessary for arachidonic acid release. A23187 and okadaic acid activate cPLA2by different mechanisms, yet both induce translocation to the nuclear envelopein Sf9 cells. The results demonstrate that alternative regulatory pathways canlead to cPLA2 activation and arachidonic acid release.
PMID
10080535
|
|