| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
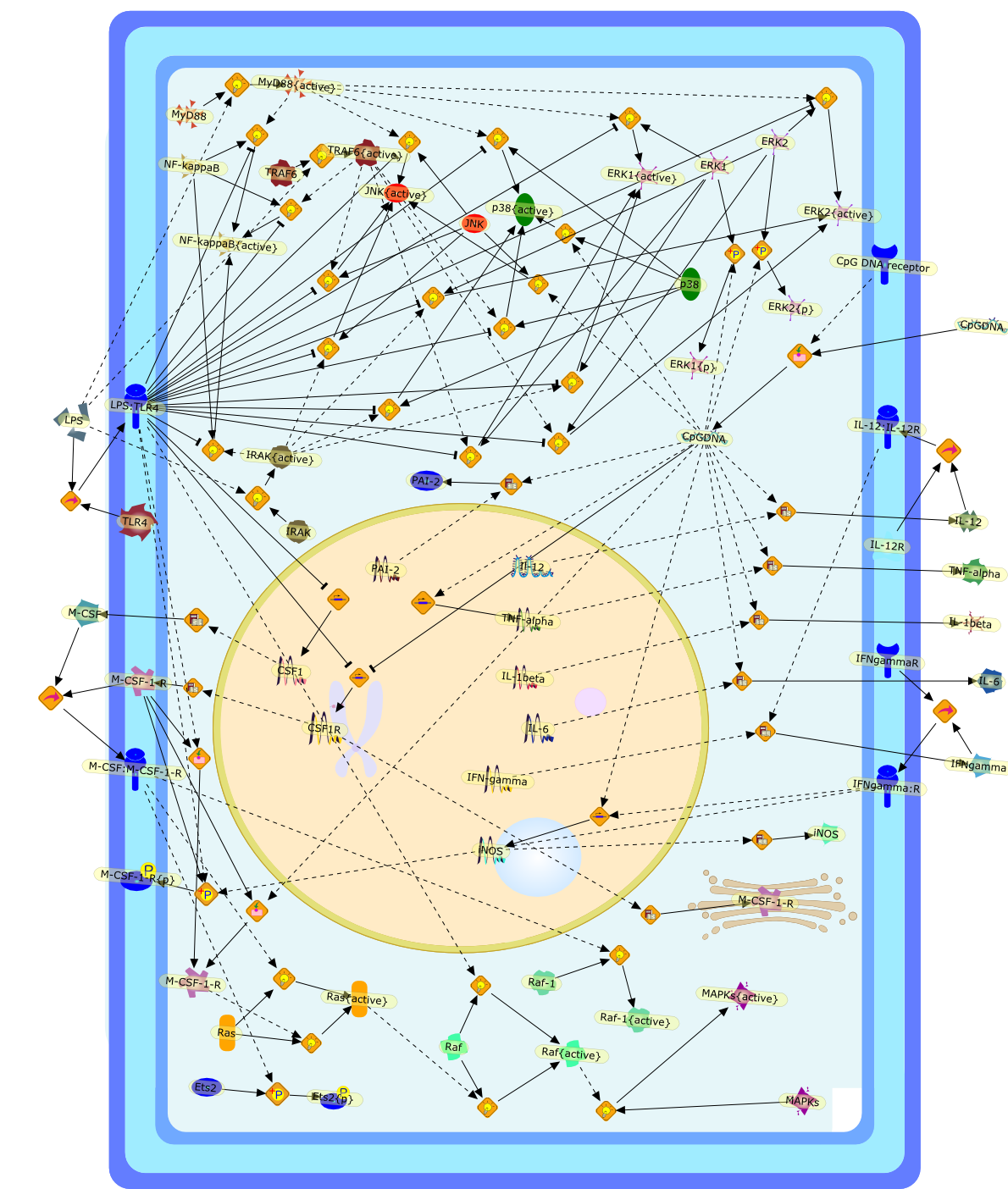
The actions of bacterial DNA on murine macrophages.
Affiliation
Centre for Molecular and Cellular Biology, and Department of Microbiology,University of Queensland, Australia.
Abstract
Murine macrophages are able to distinguish bacterial from mammalian DNA. Theresponse is mimicked by single-stranded oligonucleotides containing unmethylatedCG dinucleotides ("CpG" motifs) in specific sequence contexts. The dose-responsecurve for activation is influenced by variation in the sequence flanking thecore CpG motif. CpG or bacterial DNA activates several signaling pathways incommon with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), leading to induction of cytokinegenes such as tumor necrosis factor alpha. Pretreatment with LPS causesdesensitization to subsequent activation by CpG DNA. Both stimuli also causecell cycle arrest in macrophages proliferating in response to the macrophagegrowth factor colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1), but prevent apoptosis causedby growth factor removal. In part, cell cycle arrest by CpG DNA and LPS may belinked to rapid down-modulation of the CSF-1 receptor from the cell surface, aresponse that occurs in an all-or-nothing manner. The response of macrophages toCpG DNA has aspects in common with the DNA damage response in other cell types,which may provide clues to the underlying mechanism.
PMID
10534106
|