| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Cellular signaling in macrophage migration and chemotaxis.
Affiliation
The Randall Centre for Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Function, King's CollegeLondon, United Kingdom. gareth.jones@kcl.ac.uk
Abstract
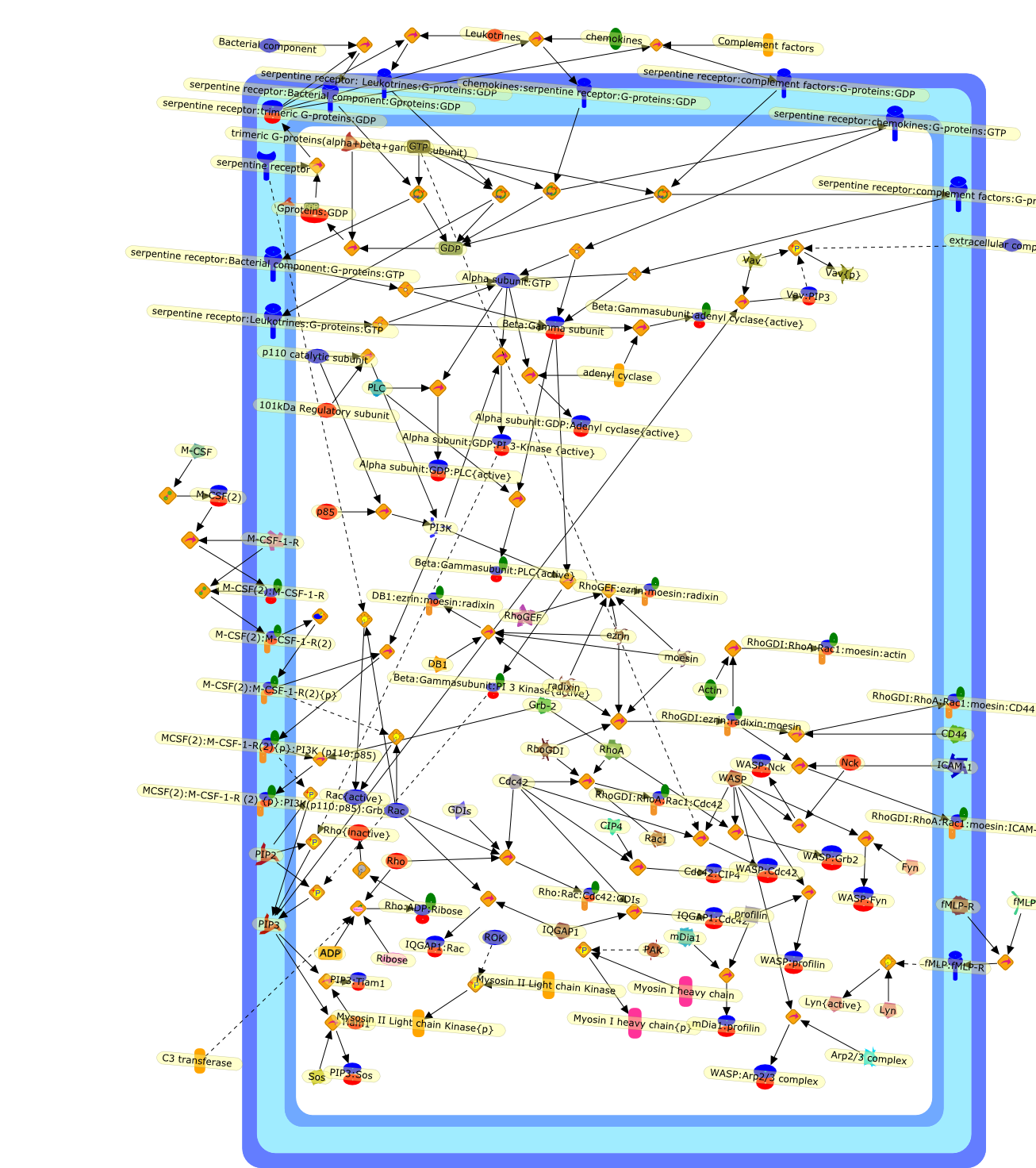
Whereas most cells in adult tissues are fixed in place by cell junctions,leukocytes are motile and able to migrate actively through the walls of bloodvessels into surrounding tissues. The actin cytoskeleton of these cells plays acentral role in locomotion, phagocytosis, and the regulation of cell shape thatare crucial elements of neutrophil and monocyte/macrophage function. This reviewwill concentrate on how macrophages in particular control the actin cytoskeletonto generate cell movement and the shape changes required for chemotaxis. It hasrecently become evident that a complex of seven proteins known as the Arp2/3complex regulates the assembly of new actin filament networks at the leadingfront of moving cells. Proteins of the Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP)family bind directly to the Arp2/3 complex and stimulate its ability to promotethe nucleation of new actin filaments. Upstream of the WASP family proteins,receptor tyrosine kinases, G-protein-coupled receptors, phosphoinositide-3-OHkinase (PI 3-kinase), and the Rho family of GTPases receive and transduce thesignals that lead to actin nucleation through WASP-Arp2/3 action. Although manygaps remain in our understanding, we are now in a position to considercompleting signaling pathways that are initiated from outside the cell to theactin rearrangements that drive cell motility and chemotaxis.
PMID
11073096
|