| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Induction of proliferation and cytokine production in human T lymphocytes bylipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Affiliation
Department of Immunology and Cell Biology, Division of Cellular Immunology,Research Center Borstel, Parkallee 22, 23845, Borstel, Germany.ajulmer@fz-borstel.de
Abstract
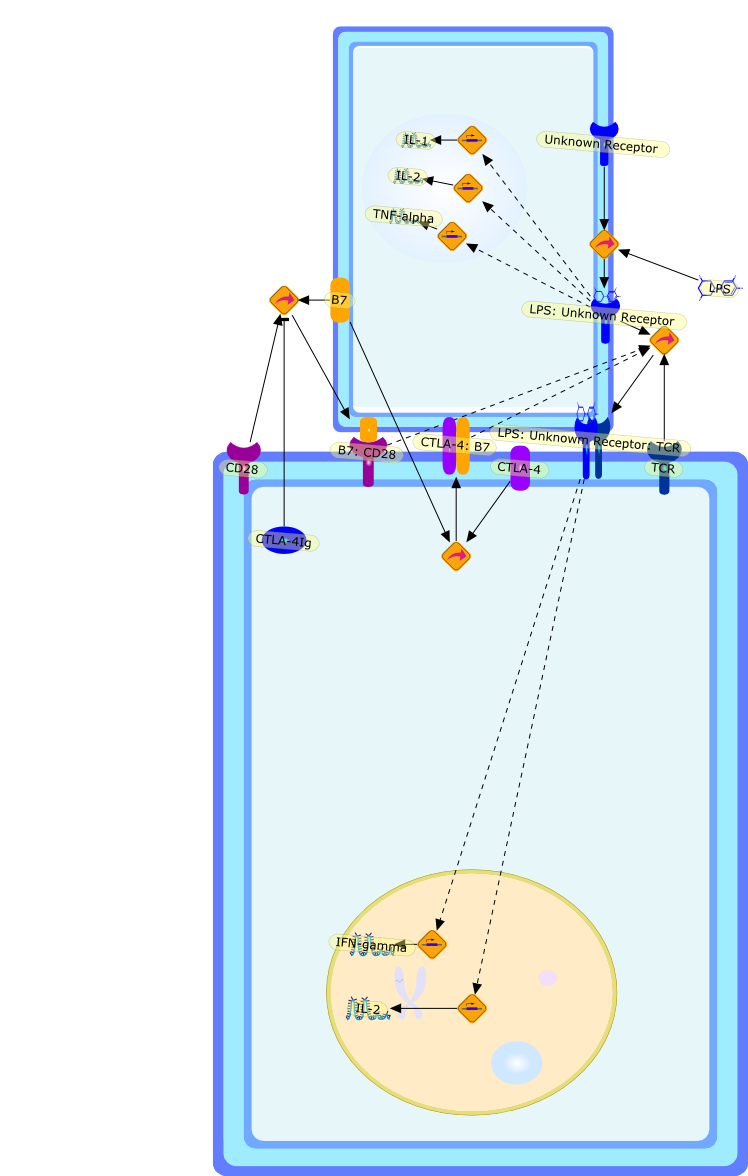
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also known as endotoxin, is a compound of the cellwall of Gram-negative bacteria, which has been demonstrated to induceinflammatory reactions in vitro as well as in vivo, including lethal shock. Agreat number of different cells have been documented to be reactive to LPS, e.g.monocytes/macrophages, vascular cells, polymorphonuclear cells, and even Blymphocytes. We have now established that T lymphocytes could also contribute toan inflammatory reaction to LPS. LPS is a potent inducer of human T-lymphocyteproliferation and cytokine production. The activation of T lymphocytes by LPSrequires direct cell-to-cell contact with viable accessory monocytes. Thisinteraction was found to be MHC-unrestricted, but strongly dependent oncostimulatory signals provided by B7/CD28 interactions. The frequency ofresponding T lymphocytes is less than 1:1000. A very exciting finding was thatnot only monocytes, but also CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells, which circulate inperipheral blood in very low frequency, exert essential accessory cell activityduring stimulation of T lymphocytes by LPS. In contrast, the response of Tlymphocytes to conventional recall antigens is not controlled by blood stemcells. These conclusions are based on the observation that depletion ofCD34-positive blood stem cells resulted in a complete loss of LPS-inducedT-lymphocyte stimulation. Addition of CD34-enriched blood stem cells led to arecovery of reactivity of T lymphocyte to LPS. The characteristics ofT-lymphocyte activation indicate that LPS is neither active as a mitogen, or asa superantigen, or as a classical antigen, but may activate T lymphocyte througha new, so far undescribed, mechanism. Furthermore, the involvement ofhematopoietic blood stem cells in the activation of T lymphocytes by LPSdemonstrates a role of these cells in inflammatory and immunological events.
PMID
11090938
|