| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes.
Affiliation
Departments of Immunology, C-204, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 NorthTorrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Abstract
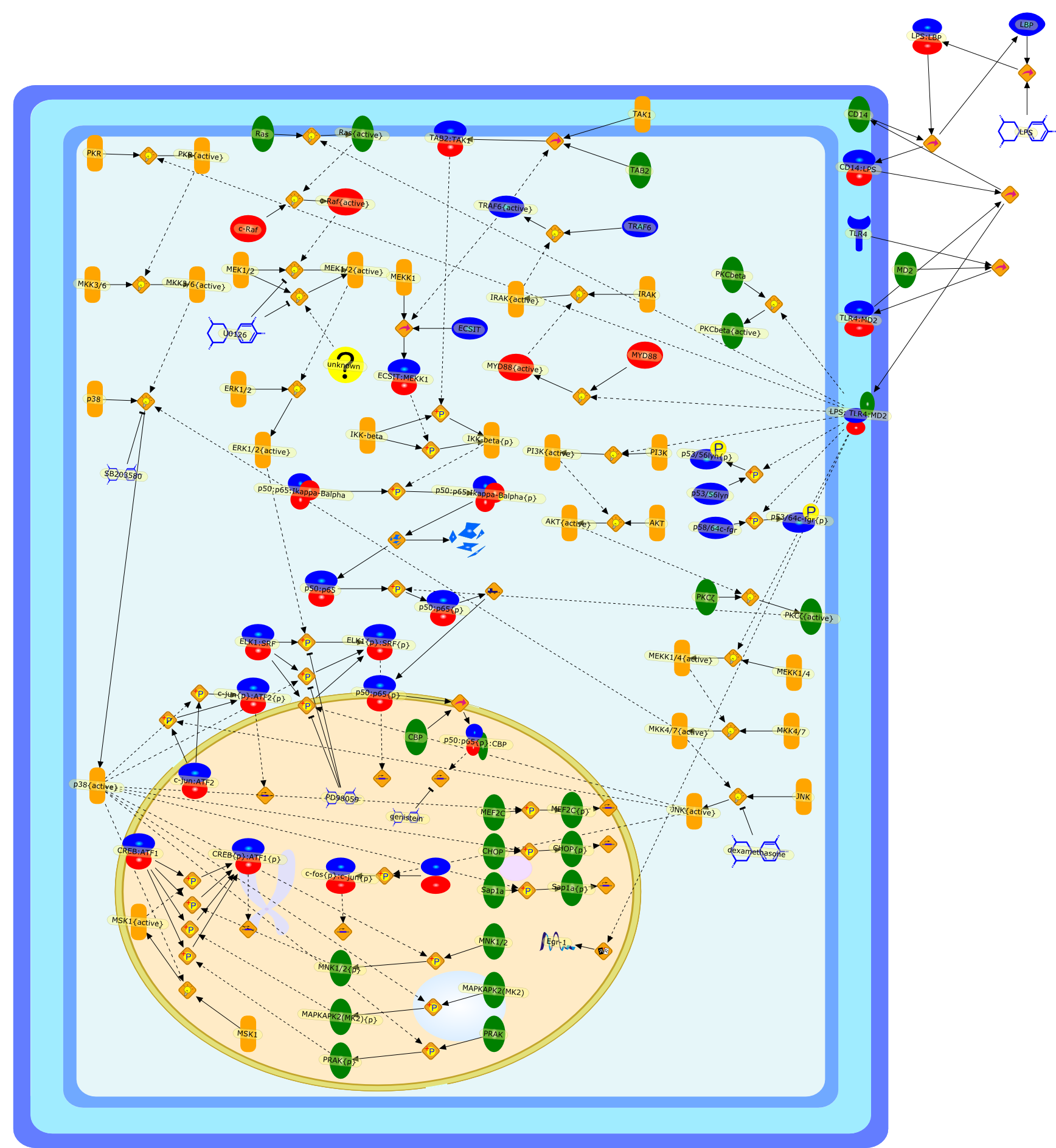
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS [endotoxin]) is the principal component of the outermembrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Recent studies have elucidated how LPS isrecognized by monocytes and macrophages of the innate immune system. Humanmonocytes are exquisitely sensitive to LPS and respond by expressing manyinflammatory cytokines. LPS binds to LPS-binding protein (LBP) in plasma and isdelivered to the cell surface receptor CD14. Next, LPS is transferred to thetransmembrane signaling receptor toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and its accessoryprotein MD2. LPS stimulation of human monocytes activates several intracellularsignaling pathways that include the IkappaB kinase (IKK)-NF-kappaB pathway andthree mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways: extracellularsignal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1 and 2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38.These signaling pathways in turn activate a variety of transcription factorsthat include NF-kappaB (p50/p65) and AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun), which coordinate theinduction of many genes encoding inflammatory mediators.
PMID
11257452
|