| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
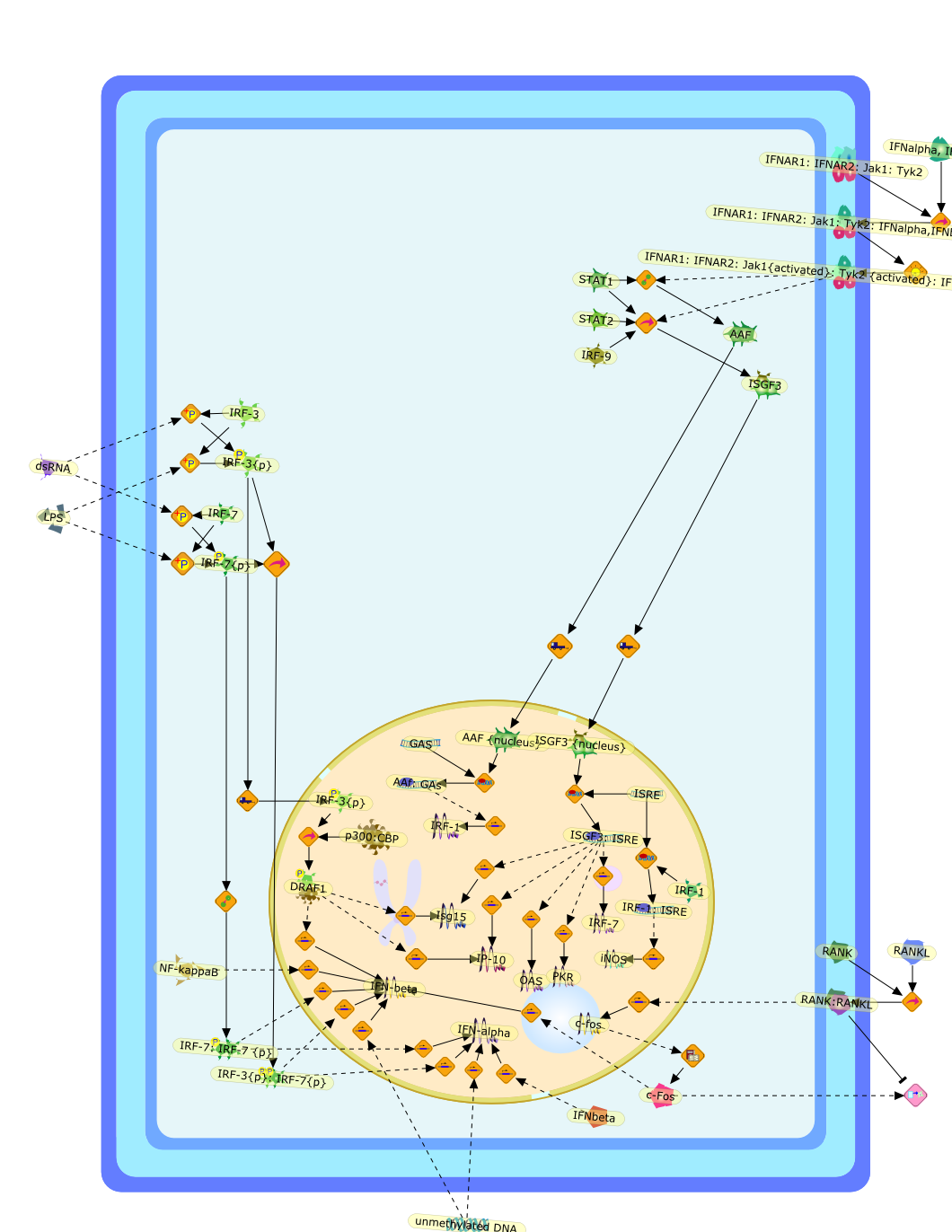
The interferon-alpha/beta system in antiviral responses: a multimodal machineryof gene regulation by the IRF family of transcription factors.
Affiliation
Department of Immunology, Faculty of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine,University of Tokyo, Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, 113-0033, Tokyo, Japan.tada@m.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Abstract
The efficient induction of interferons alpha and beta (IFN-alpha/beta) invirus-infected cells is central to the antiviral response of a host and isregulated mainly at the level of gene transcription. Once produced,IFN-alpha/beta transmit signals to the cell interior via a specific receptorcomplex to induce an antiviral response. Recently, the auto-amplificationmechanism of the IFN-alpha/beta system that follows viral infection has beenidentified. This mechanism is mediated by transcription factors of the IFNregulatory factor family and, in fact, may have evolved to render the systemmore robust in antiviral responses.
PMID
11790540
|