| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
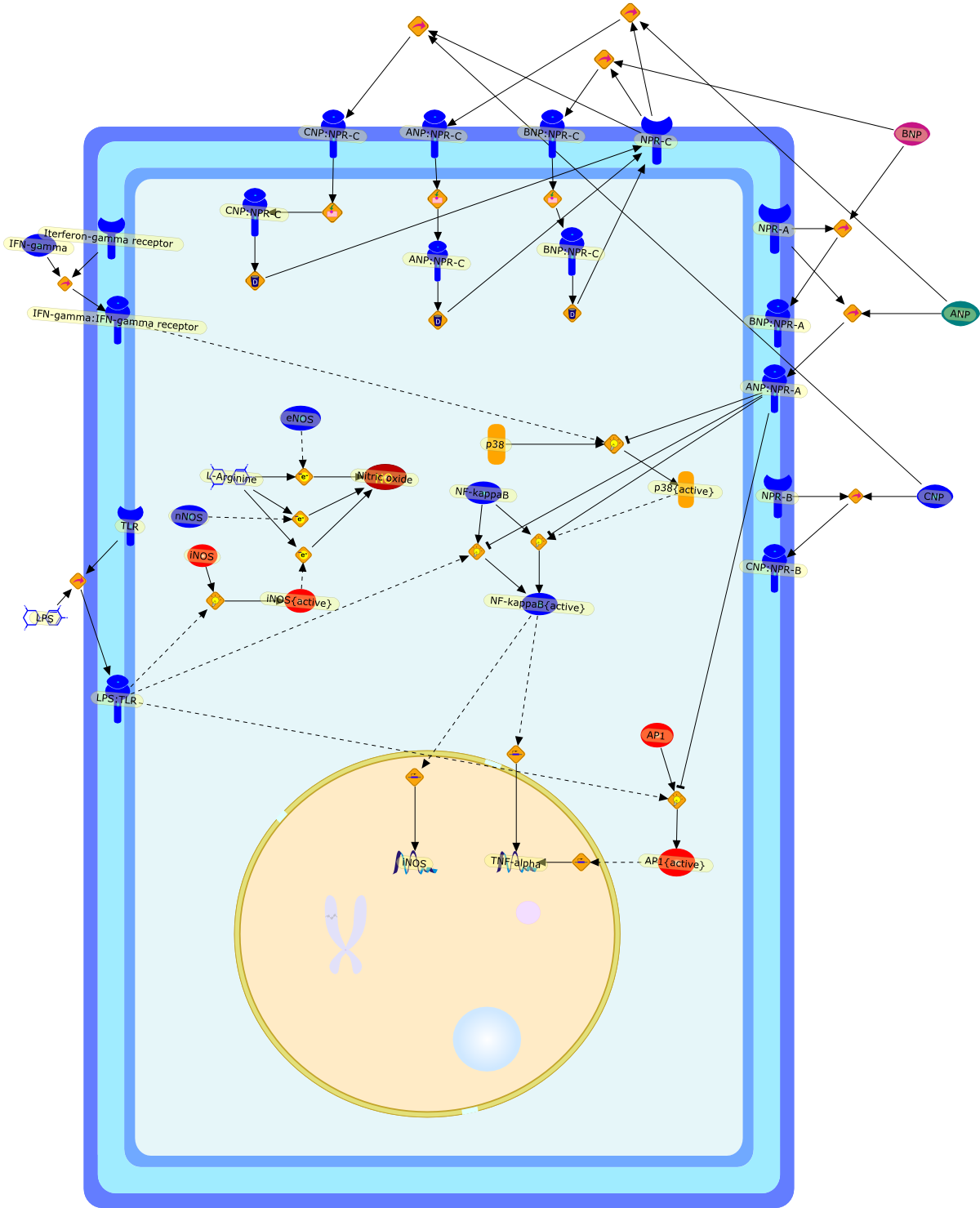
The atrial natriuretic peptide regulates the production of inflammatorymediators in macrophages.
Affiliation
Department of Pharmacy, Centre of Drug Research, University of Munich, Germany.Alexandra.Kiemer@cup.uni-muenchen.de
Abstract
The atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), a member of the natriuretic peptidefamily, is a cardiovascular hormone which possesses well defined natriuretic,diuretic, and vasodilating properties. Most of the biological effects of ANParemediated through its guanylyl cyclase coupled A receptor. Because ANP and itsreceptors have been shown to be expressed and differentially regulated in theimmune system, it has been suggested that ANP has an immunomodulatory potency.Much investigation of the effects of ANP on the activation of macrophages hasbeen carried out. ANP was shown to inhibit the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-inducedexpression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in macrophages in anautocrine fashion. ANP in this context was shown to reduce significantly theactivation of NF-kappaB and to destabilise iNOS mRNA. ANP, furthermore, cansignificantly reduce the LPS-induced secretion of tumour necrosis factor alpha(TNFalpha) in macrophages. The relevance of these findings on a regulatory rolefor ANP on TNFalpha in humans was shown by the fact that ANP significantlyreduces the release of TNFalpha in whole human blood. It was furthermore shownto attenuate the release of interleukin 1beta (IL1beta). Interestingly, ANP didnot affect the secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL10 and IL1receptor antagonist (IL1ra). In summary, ANP was shown to reduce the secretionof inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Therefore, this cardiovascular hormonemay possess anti-inflammatory potential.
PMID
11890659
|