| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Macrophage-stimulating protein and RON receptor tyrosine kinase: potentialregulators of macrophage inflammatory activities.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine and Immunology, University of Colorado Health SciencesCenter and Denver Health Medical Center, Denver, CO, USA.ming-hai.wang@uchsc.edu
Abstract
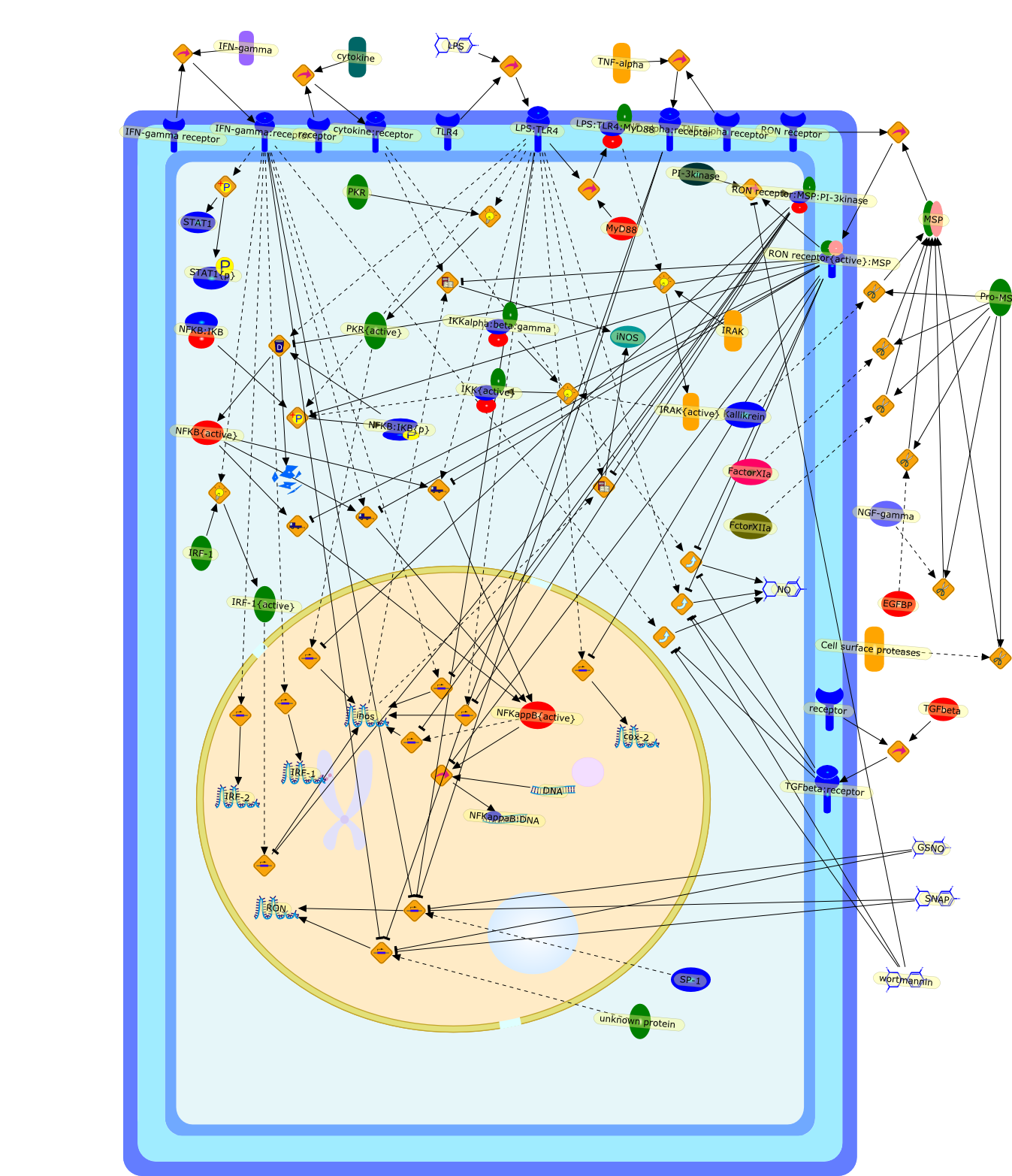
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) is a serum protein belonging to theplasminogen-related growth factor family. The specific receptor for MSP is theRON (recepteur d'origine nantais) receptor tyrosine kinase - a member of the METproto-oncogene family. Activation of RON by MSP exerts dual functions onmacrophages. The stimulatory activities include the induction of macrophagespreading, migration and phagocytosis. However, MSP also inhibitslipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of inflammatory mediators, includinginducible nitric oxide and prostaglandins. These suppressive effects aremediated by RON-transduced signals that block LPS-induced enzymatic cascadesthat activate nuclear factor kappa-B (NFkappaB) pathways. Recent in vivo studiesdemonstrated that inactivation of the RON gene results in increased inflammatoryresponses and susceptibility to LPS-induced septic death in mice, suggestingthat RON expression is required for attenuating the extent of inflammatoryresponses in vivo. Thus, MSP and RON are potential regulators that controlmacrophage activities during bacterial infection in vivo.
PMID
12472665
|