| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signalingpathways.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Abstract
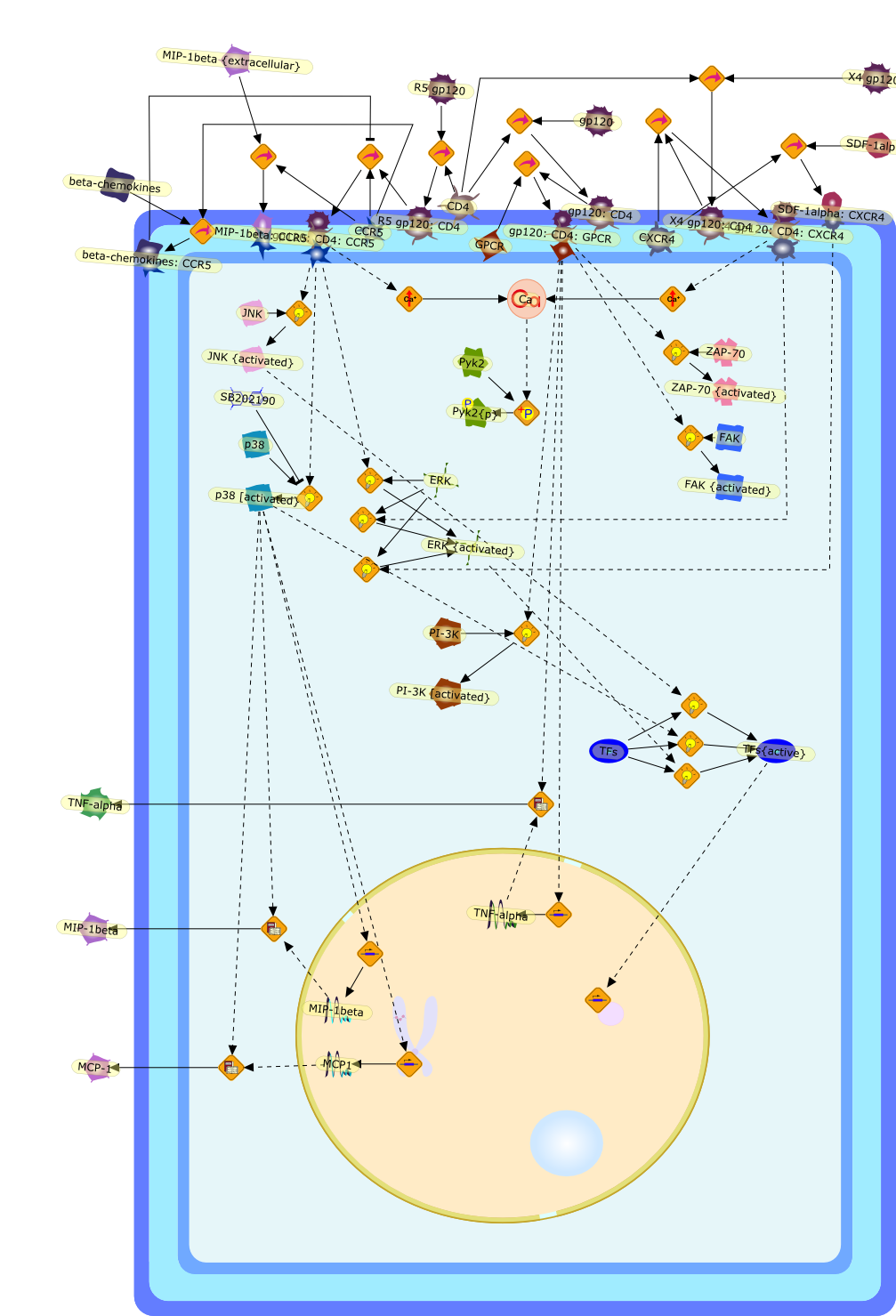
Macrophages are major targets for infection by human immunodeficiency virus type1 (HIV-1). In addition to their role as productive viral reservoirs,inappropriate activation of infected and uninfected macrophages appears tocontribute to pathogenesis. HIV-1 infection requires initial interactionsbetween the viral envelope surface glycoprotein gp120, the cell-surface proteinCD4, and a chemokine receptor CCR5 or CXCR4. Besides their role in HIV-1 entry,CCR5 and CXCR4 are G protein-coupled receptors that can activate multipleintracellular signaling pathways. HIV-1 gp120 has been shown to activatesignaling pathways through the chemokine receptors in several cell typesincluding lymphocytes, neurons, and astrocytes. In some cell types, theseconsequences may cause cellular injury. In this review, we highlight our datademonstrating diverse signaling events that occur in primary human macrophagesin response to gp120/chemokine receptor interactions. These responses includeK+, Cl-, and nonselective cation currents, intracellular Ca2+ increases, andactivation of several kinases including the focal adhesion-related tyrosinekinase Pyk2, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), and phosphoinositol-3kinase. Activation of the MAPK leads to gp120-induced expression of chemokinessuch as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage-inflammatoryprotein-1beta and the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha.These responses establish a complex cytokine network, which may enhance orsuppress HIV-1 replication. In addition, dysregulation of macrophage function bygp120/chemokine receptor signaling may contribute to local inflammation andinjury and further recruit additional inflammatory and/or target cells.Targeting these cellular signaling pathways may have benefit in controllinginflammatory sequelae of HIV infection such as in neurological disease.
PMID
12960231
|