| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
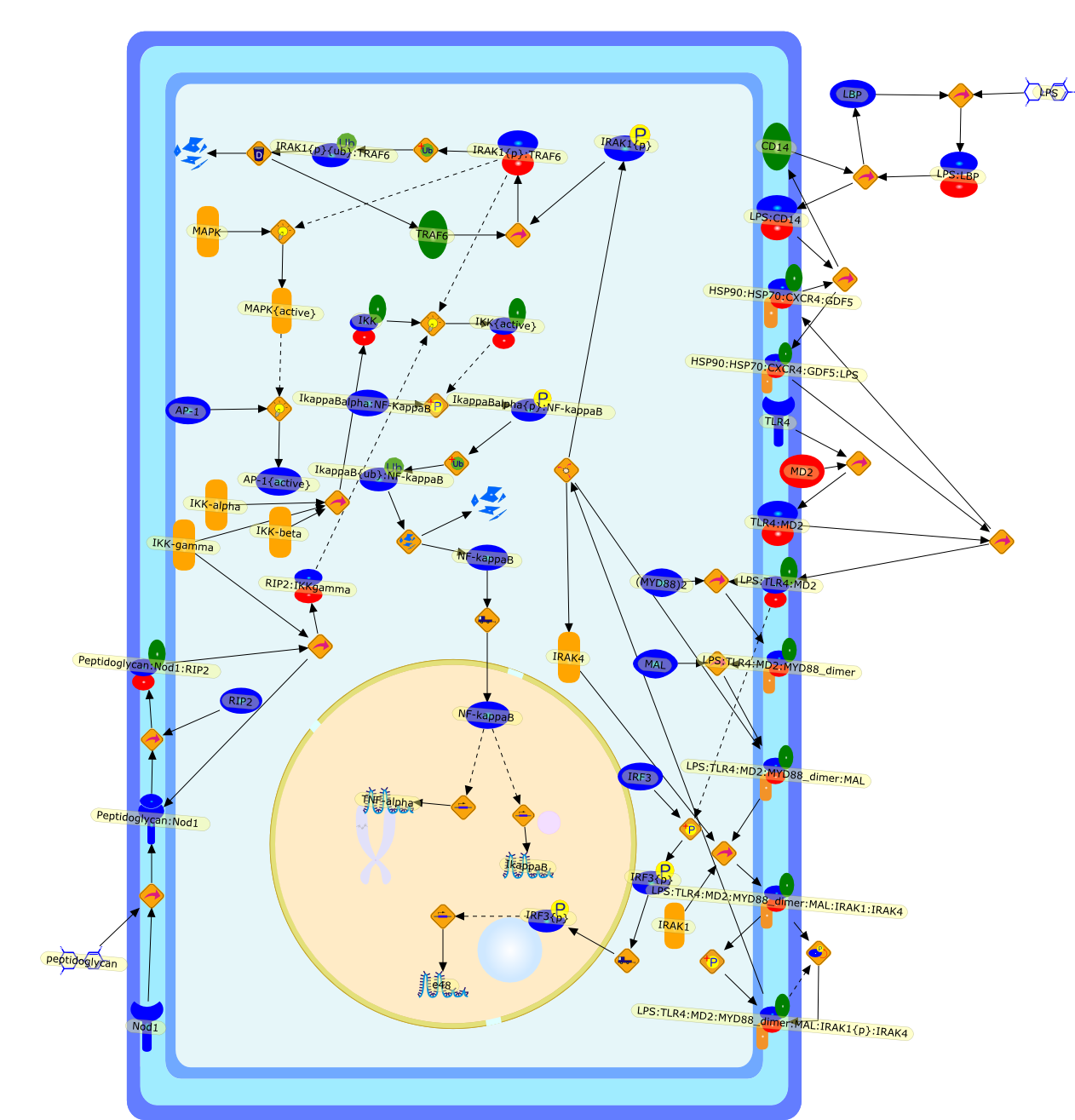
Molecular mechanisms of macrophage activation and deactivation bylipopolysaccharide: roles of the receptor complex.
Affiliation
Japanese Red Cross, Hokkaido Red Cross Blood Center, Yamanote 2-2, Nishi-ku,Sapporo 063-0002, Japan. fujihara@hokkaido.bc.jrc.or.jp
Abstract
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the major structural component of the outerwall of Gram-negative bacteria, is a potent activator of macrophages. Activatedmacrophages produce a variety of inflammatory cytokines. Excessive production ofcytokines in response to LPS is regarded as the cause of septic shock. On theother hand, macrophages exposed to suboptimal doses of LPS are rendered tolerantto subsequent exposure to LPS and manifest a profoundly altered response to LPS.Increasing evidence suggests that monocytic cells from patients with sepsis andseptic shock survivors have characteristics of LPS tolerance. Thus, anunderstanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying activation and deactivationof macrophages in response to LPS is important for the development oftherapeutics for septic shock and the treatment of septic shock survivors. Overthe past several years, significant progress has been made in identifying andcharacterizing several key molecules and signal pathways involved in theregulation of macrophage functions by LPS. In this paper, we summarize thecurrent findings of the functions of the LPS receptor complex, which is composedof CD14, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), and myeloid differentiation protein-2(MD-2), and the signal pathways of this LPS receptor complex with regard to bothactivation and deactivation of macrophages by LPS. In addition, recenttherapeutic approaches for septic shock targeting the LPS receptor complex aredescribed.
PMID
14609719
|