| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and host innate immune responses tomicrobes.
Affiliation
Division of infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, CentreHospitalier Universitaire Vaudois, Lausanne, Switzerland.Thierry.Calandra@chuv.hospvd.ch
Abstract
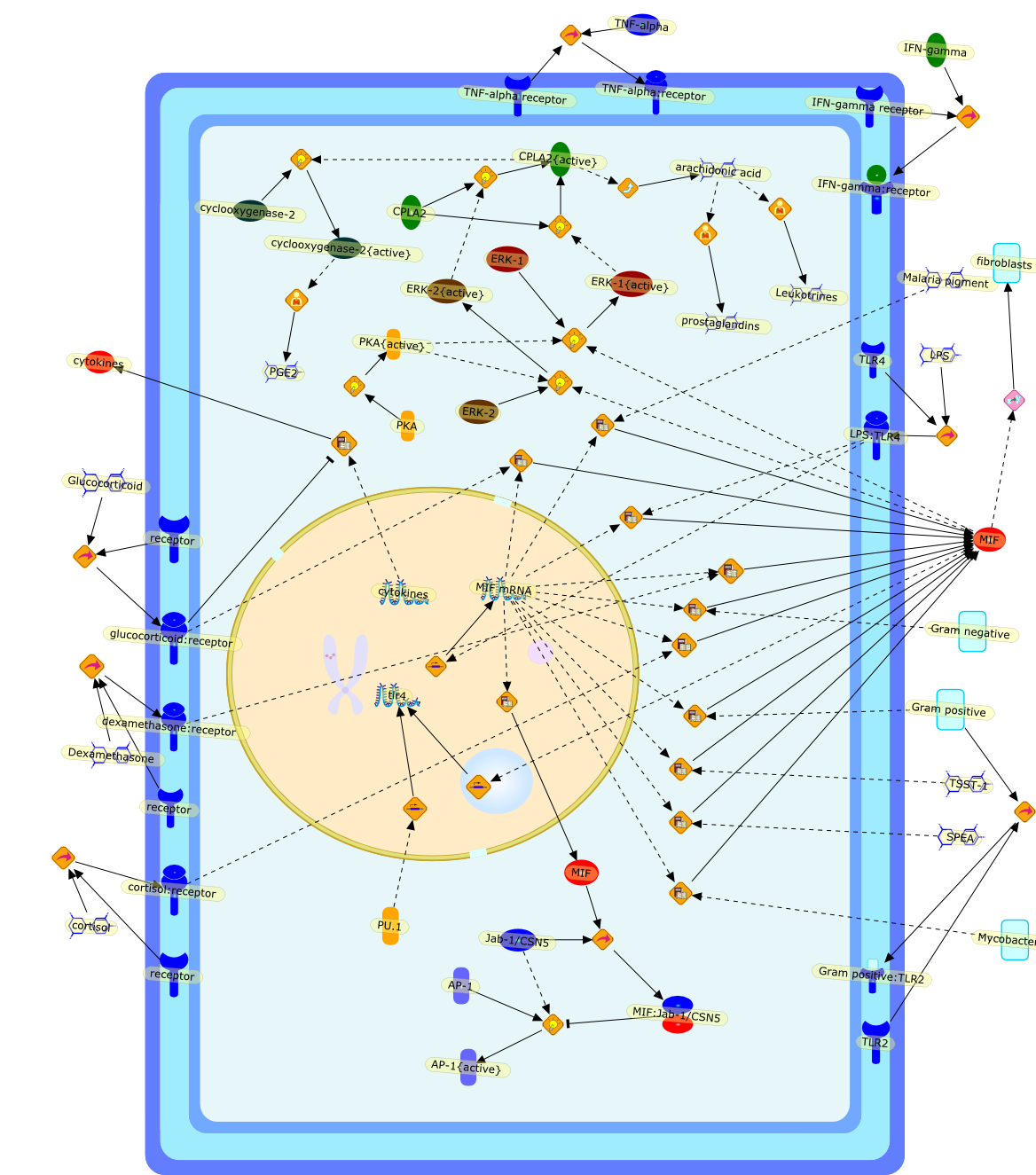
Among innate immune cells, macrophages play an essential role in the sensing andelimination of invasive microorganisms. Binding of microbial products topathogen-recognition receptors stimulates macrophages to release cytokines andother effector molecules that orchestrate the host innate and adaptive immuneresponses. Recently, the protein known as macrophage migration inhibitory factor(MIF) has emerged as a pivotal mediator of innate immunity. First identified asa T-cell cytokine, MIF was rediscovered as a protein released by pituitary cellsafter exposure to endotoxin [lipopolysaccharide (LPS)] or bacteria and inresponse to stress. Monocytes, macrophages and lymphocytes constitutivelyexpress MIF, which is rapidly released after stimulation with bacterialendotoxins and exotoxins, and cytokines. MIF induces powerful proinflammatorybiological responses and has been shown to be an important effector molecule ofseptic shock. High levels of MIF have been detected in the circulation ofpatients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Inhibition of MIF activity withneutralizing anti-MIF antibodies or deletion of the Mif gene led to a markedreduction in cytokine production and protected mice from lethal bacterial sepsisand toxic shock induced by Gram-negative endotoxin or Gram-positive exotoxins.Investigations into the mechanisms whereby MIF modulates innate immune responsesto endotoxin and Gram-negative bacteria have shown that MIF up-regulates theexpression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), the signal-transducing molecule ofthe LPS receptor complex. Thus, MIF enables cells, such as the macrophage, thatare at the forefront of the host antimicrobial defences, to sense promptly thepresence of invading Gram-negative bacteria and mount an innate immune response.Given that it is a pivotal regulator of innate immune responses to bacterialinfections, MIF appears to be a perfect target for novel therapeuticinterventions in patients with severe sepsis.
PMID
14620137
|