| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
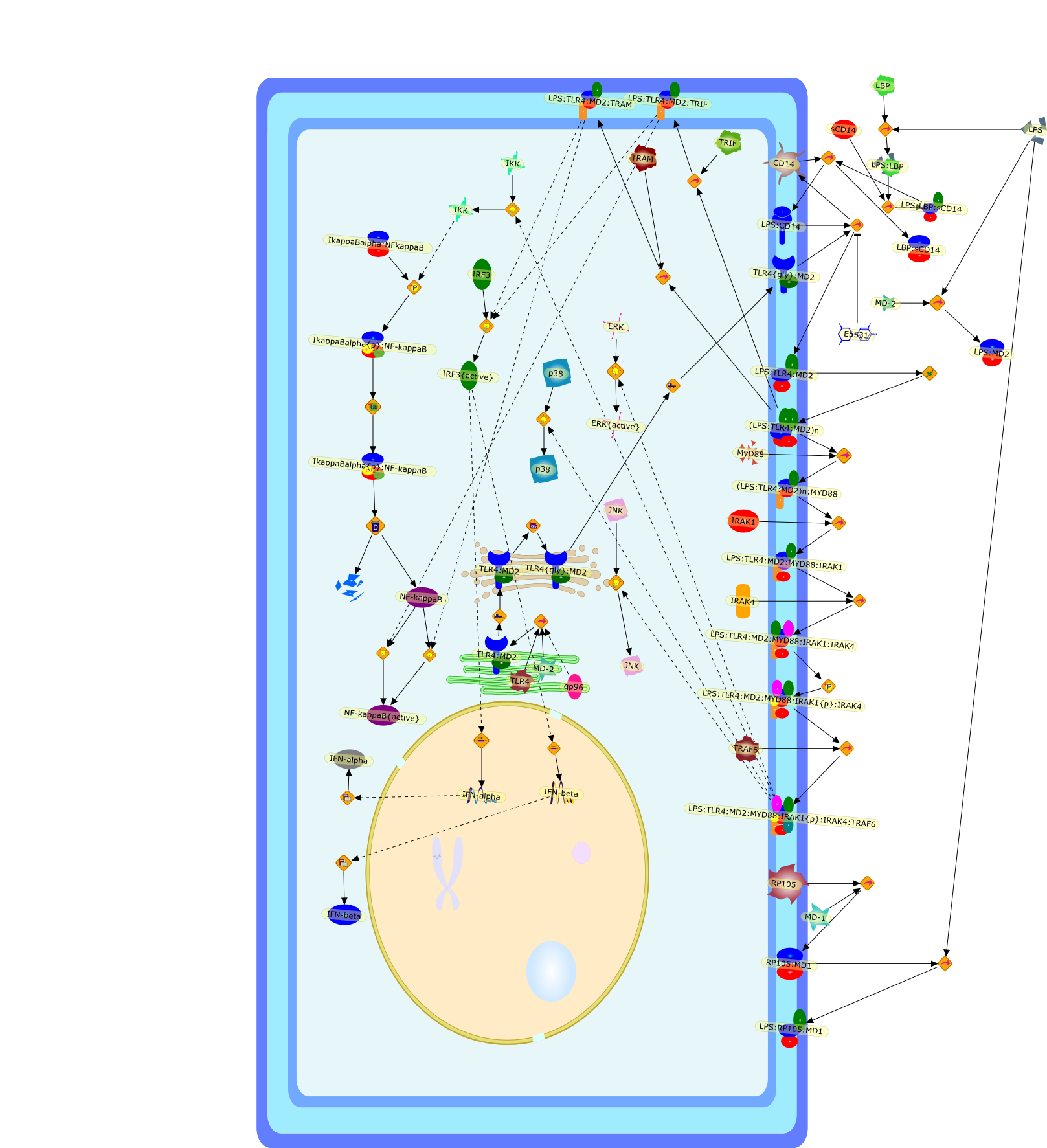
Innate recognition of lipopolysaccharide by Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2.
Affiliation
Division of Infectious Genetics, Department of Microbiology and Immunology,Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, 4-6-1 Shirokanedai, Tokyo108-8639, Japan. kmiyake@ims.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are pathogen recognition molecules that activate theimmune system as part of the innate immune response. Microbial recognition byTLRs plays a crucial role in the host immune system's decision to respond or notto a particular microbial infection. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a membraneglycolipid of Gram-negative bacteria, exhibits strong immunostimulating activityamong TLR ligands and has been studied in great detail. Recent studies haveshown that cell surface TLR4-MD-2 physically interacts with LPS and triggers therelease of an LPS signal, revealing a host-pathogen interaction mediated by TLR.
PMID
15051069
|