| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors and the host defense against microbial pathogens: bringingspecificity to the innate-immune system.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine, University Medical Center St. Radboud, NijmegenUniversity, The Netherlands. M.Netea@aig.umcn.nl
Abstract
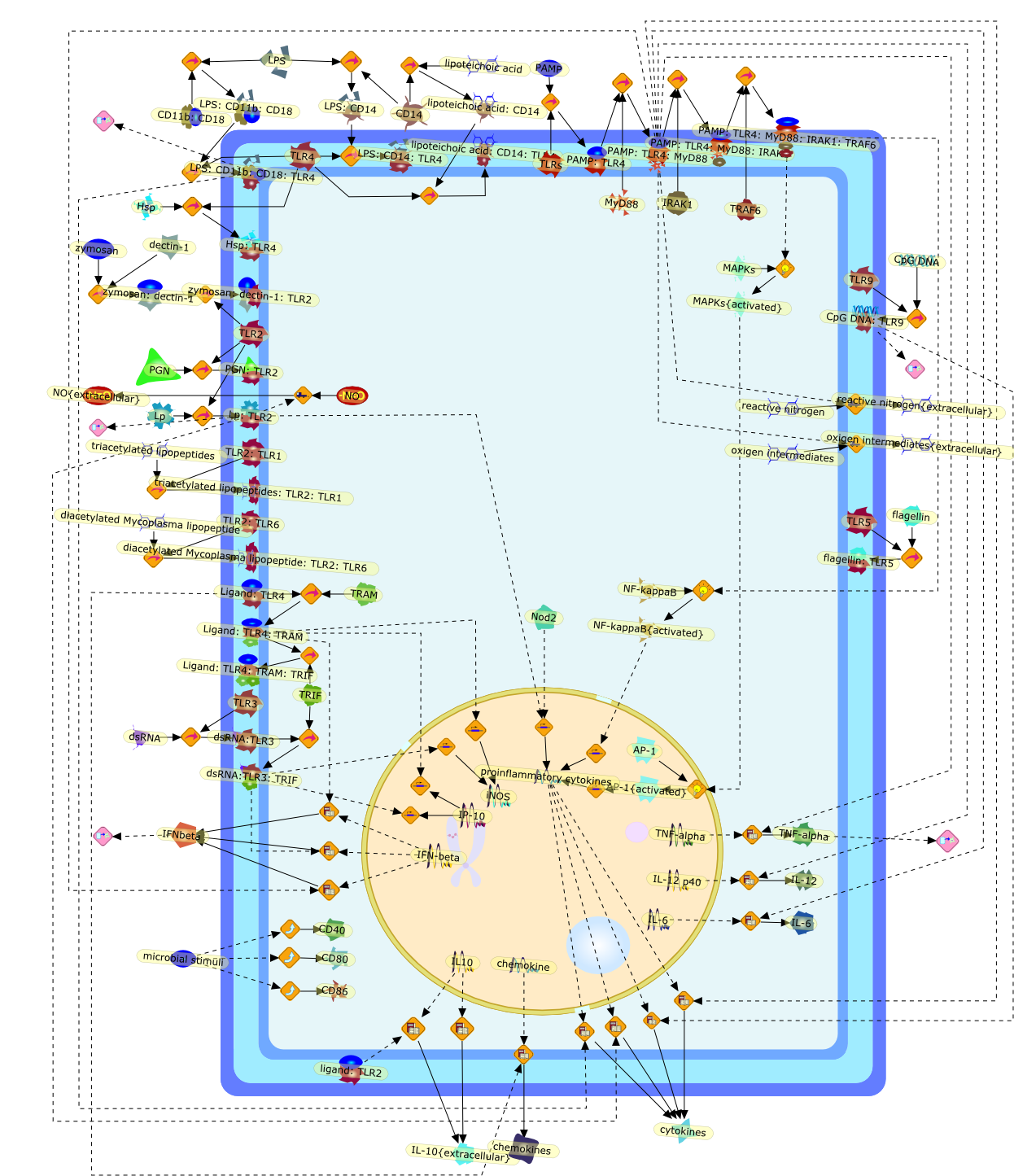
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have been identified as a major class ofpattern-recognition receptors. Recognition of pathogen-associated molecularpatterns (PAMPs) by TLRs, alone or in heterodimerization with other TLR ornon-TLR receptors, induces signals responsible for the activation of genesimportant for an effective host defense, especially proinflammatory cytokines.Although a certain degree of redundancy exists between signals induced by thevarious TLRs, recent studies have identified intracellular pathways specific forindividual TLRs. This leads to the release of cytokine profiles specific forparticular PAMPs, and thus, TLRs confer a certain degree of specificity to theinnate-immune response. In addition to the activation of the innate-immuneresponse, TLR-mediated recognition represents a link between the innate- andacquired-immune systems, by inducing the maturation of dendritic cells anddirecting the T helper responses. Alternatively, recent data have also suggestedTLR-mediated escape mechanisms used by certain pathogenic microorganisms,especially through TLR2 induction of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Finally, thecrucial role of TLRs for the host defense against infections has beenstrengthened recently by the description of patients partially defective in theTLR-activation pathways.
PMID
15075354
|