| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors.
Affiliation
Office of Research Oversight, Department of Veterans Affairs, 50 Irving Street,NW, Washington, DC 20422, USA. min-fu.tsan2@med.va.gov
Abstract
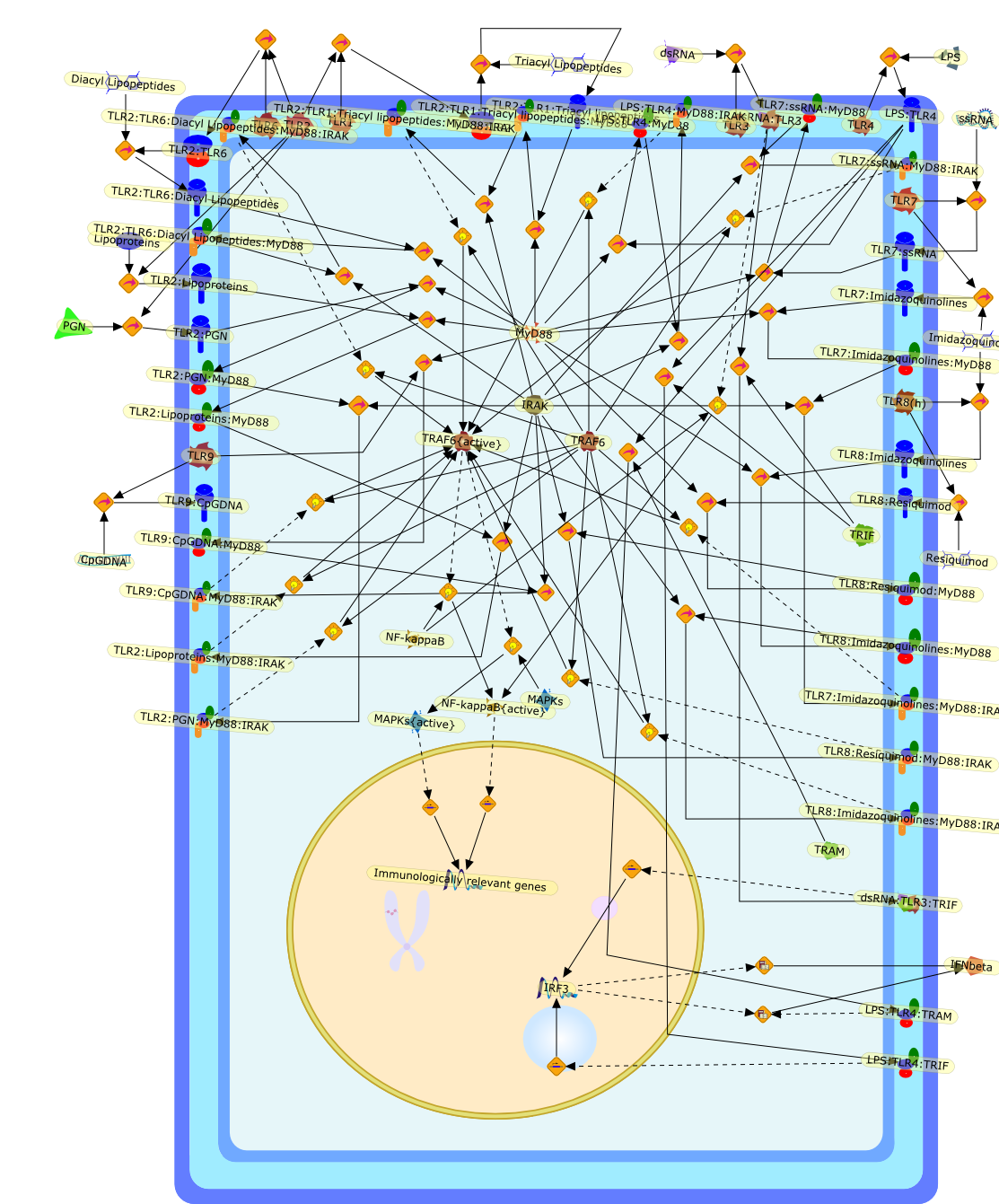
Extensive work has suggested that a number of endogenous molecules such as heatshock proteins (hsp) may be potent activators of the innate immune systemcapable of inducing proinflammatory cytokine production by themonocyte-macrophage system and the activation and maturation of dendritic cells.The cytokine-like effects of these endogenous molecules are mediated via theToll-like receptor (TLR) signal-transduction pathways in a manner similar tolipopolysaccharide (LPS; via TLR4) and bacterial lipoproteins (via TLR2).However, recent evidence suggests that the reported cytokine effects of hsp maybe a result of the contaminating LPS and LPS-associated molecules. The reasonsfor previous failure to recognize the contaminant(s) being responsible for theputative TLR ligands of hsp include failure to use highly purified hsp free ofLPS contamination; failure to recognize the heat sensitivity of LPS; and failureto consider contaminant(s) other than LPS. Whether other reported putativeendogenous ligands of TLR2 and TLR4 are a result of contamination ofpathogen-associated molecular patterns is not clear. It is essential thatefforts should be directed to conclusively determine whether the reportedputative endogenous ligands of TLRs are a result of the endogenous molecules orof contaminant(s), before exploring further the implication and therapeuticpotential of these putative TLR ligands.
PMID
15178705
|