| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Lipopolysaccharide-binding molecules: transporters, blockers and sensors.
Affiliation
Endotoxin Group, UMR-8619 of the National Center for Scientific Research,Batiment 430, University of Paris-Sud, 91405, Orsay, France.richard.chaby@bbmpc.u-psud.fr
Abstract
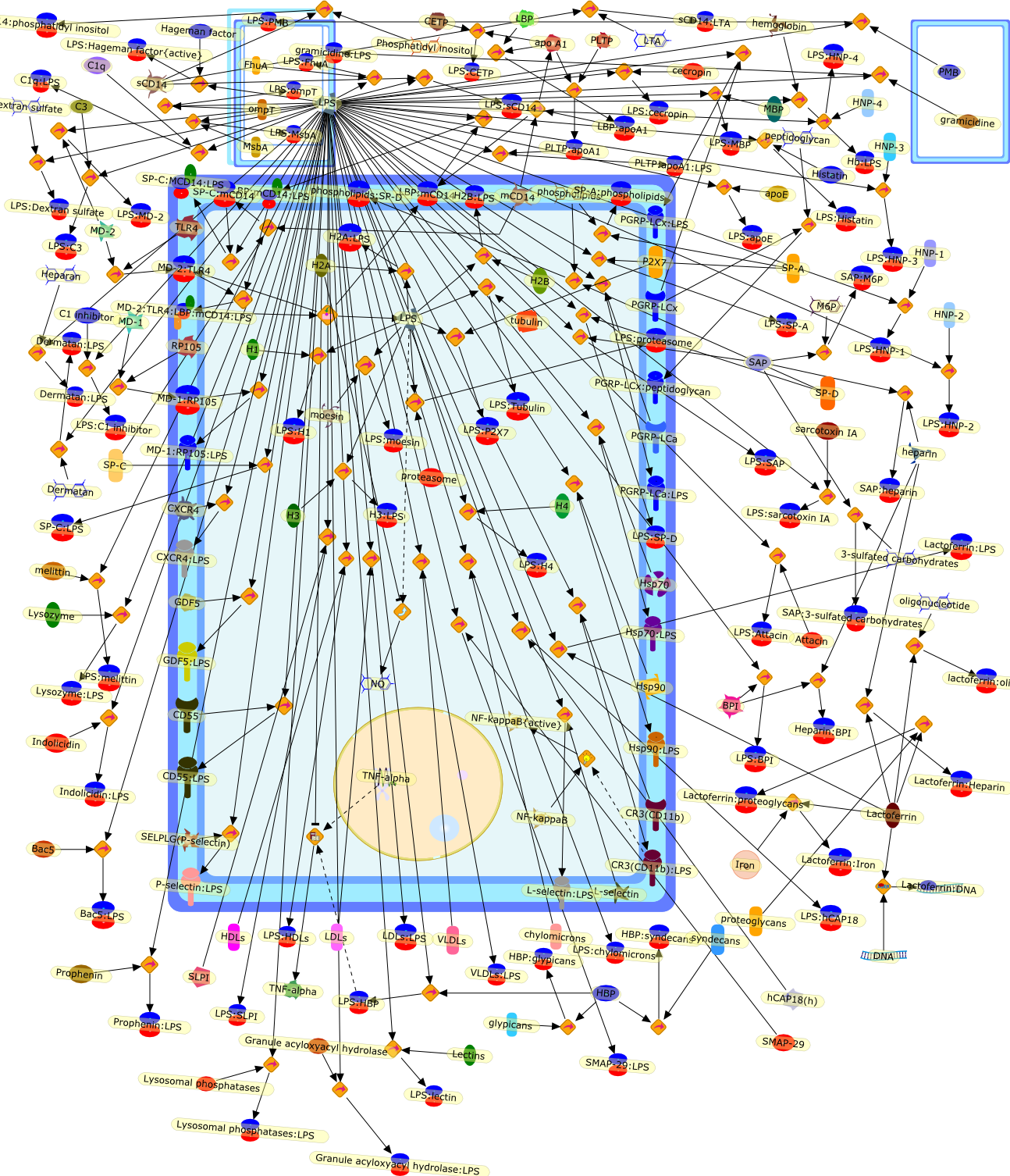
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major component of the outer membrane ofGram-negative bacteria, can be beneficial to the host by activating the innateimmune system, or harmful, by inducing inflammation, disseminated intravascularcoagulation, multiple organ failure, shock and often death. On the bacteria, andin host biological fluids and cells, LPS is never free but constantly attachedto cognate-binding proteins. Understanding how LPS is transported and furtherrecognized by sensors able to deliver a signal, or by inactivating moleculesable to neutralize its biological effects, is an important goal. This reviewdescribes the large panel of peptides and proteins reported to associate withLPS, and provides information on their origin, their structure and the locationof amino acid residues involved in their interaction with LPS. A betterunderstanding of the mode of recognition of LPS by cognate proteins promptedmany laboratories to design on a rational basis synthetic molecules which can beused to detect low amounts of endotoxin, or to act as efficient blockers of invitro and in vivo responses to LPS.
PMID
15241548
|