| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
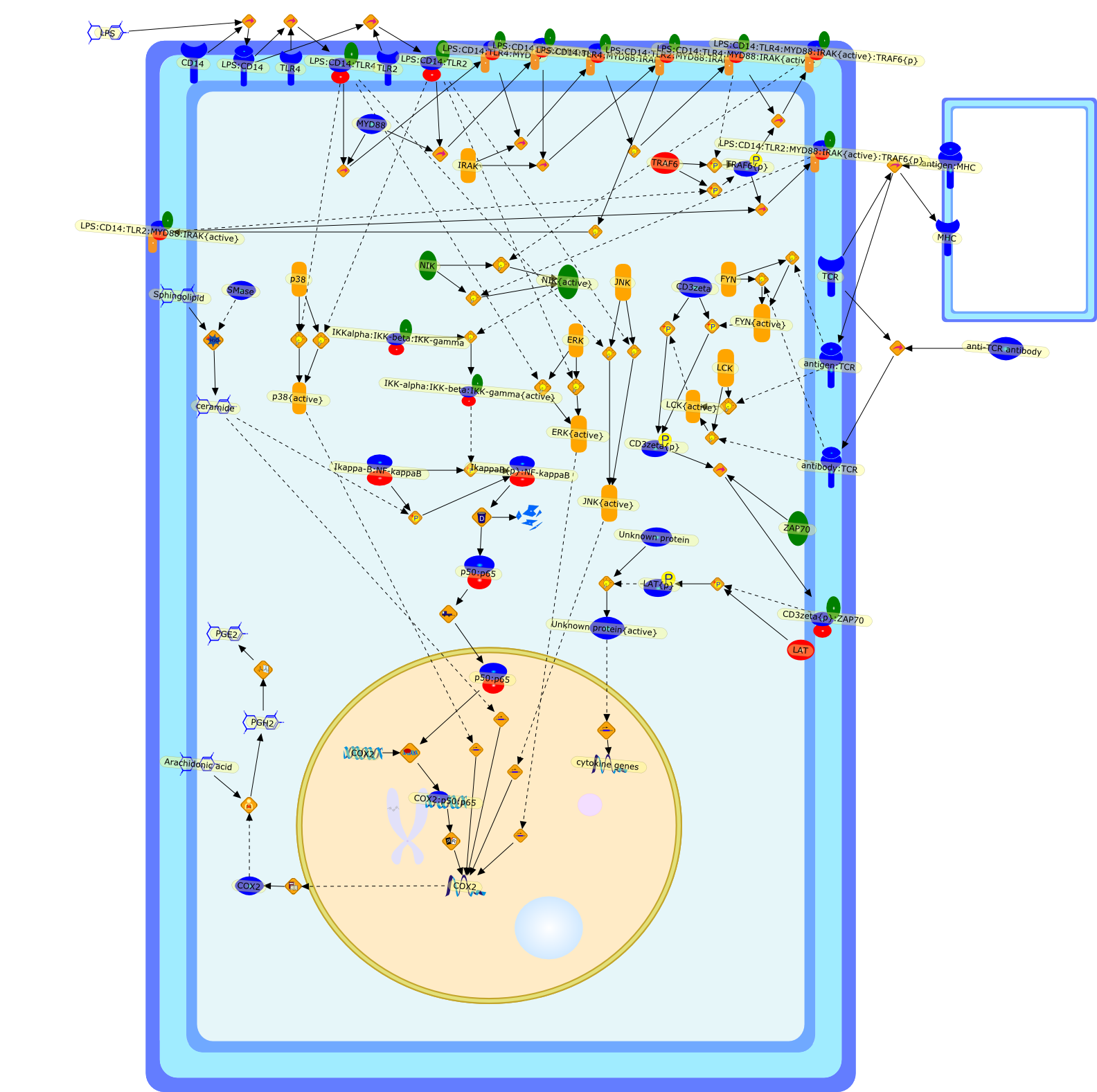
Mechanism of age-associated up-regulation in macrophage PGE2 synthesis.
Affiliation
Nutritional Immunology Laboratory, Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition ResearchCenter on Aging at Tufts University, Boston, MA 02111, USA. dayong.wu@tufts.edu
Abstract
Many physiological functions of the body change during the aging process.Dysregulated immune and inflammatory responses have been well documented in bothhumans and animals. The investigation into the cellular and molecular mechanismunderlying these disorders has provided compelling evidence that up-regulatedcyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and its product, particularly prostaglandin (PG)E2, playa critical role in the age-associated dysregulation of the immune andinflammatory responses. In particular, several studies have shown that increasedPGE2 production in old macrophages (Mphi) contributes to the suppression of Tcell function with aging. Furthermore, interventions targeted at decreasing PGE2production have been shown to enhance T cell-mediated function. COX-2 and itscatalytic products are also suggested to play a key role in age-relatedneurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Administration of anti-inflammatory drugs which inhibit COX activity has beenshown, by some investigators, to be beneficial in preventing and treating thesediseases. It is, thus, important to understand the underlying mechanisms ofage-related COX-2 up-regulation and to delineate the factors, which contributeto this age-related change. This review focuses on the regulation of PGE2production in murine Mphi; the age-associated changes in COX-2 expression; andits implication for certain disorders observed in the aged immune system andbrain. Increased PGE2 production has been shown to be mainly due to an increasein COX activity, which is, in turn, due to an increase in COX-2 protein and mRNAexpression. Elevated COX-2 mRNA represents a higher transcription rate ratherthan an altered stability of COX-2 mRNA. Upon stimulation, Mphi from old micegenerate more ceramide, a sphingolipid, than those from young mice. Ceramide hasbeen shown to induce, by itself, and also augment, LPS-stimulated COX-2expression and PGE2 production. Several lines of evidence indicate that thehigher ceramide levels in old Mphi are an important contributor to theage-associated up-regulation of COX-2 in Mphi. Ceramide up-regulates COX-2transcription by increasing activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB.Further understanding of molecular mechanisms involved in COX-2 up-regulationwill help in delineating fundamental age-related changes, which lead to thedevelopment of immune and neurological disorders in the aged.
PMID
15331118
|