| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4.
Affiliation
Department of Biochemistry, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland. palssone@tcd.ie
Abstract
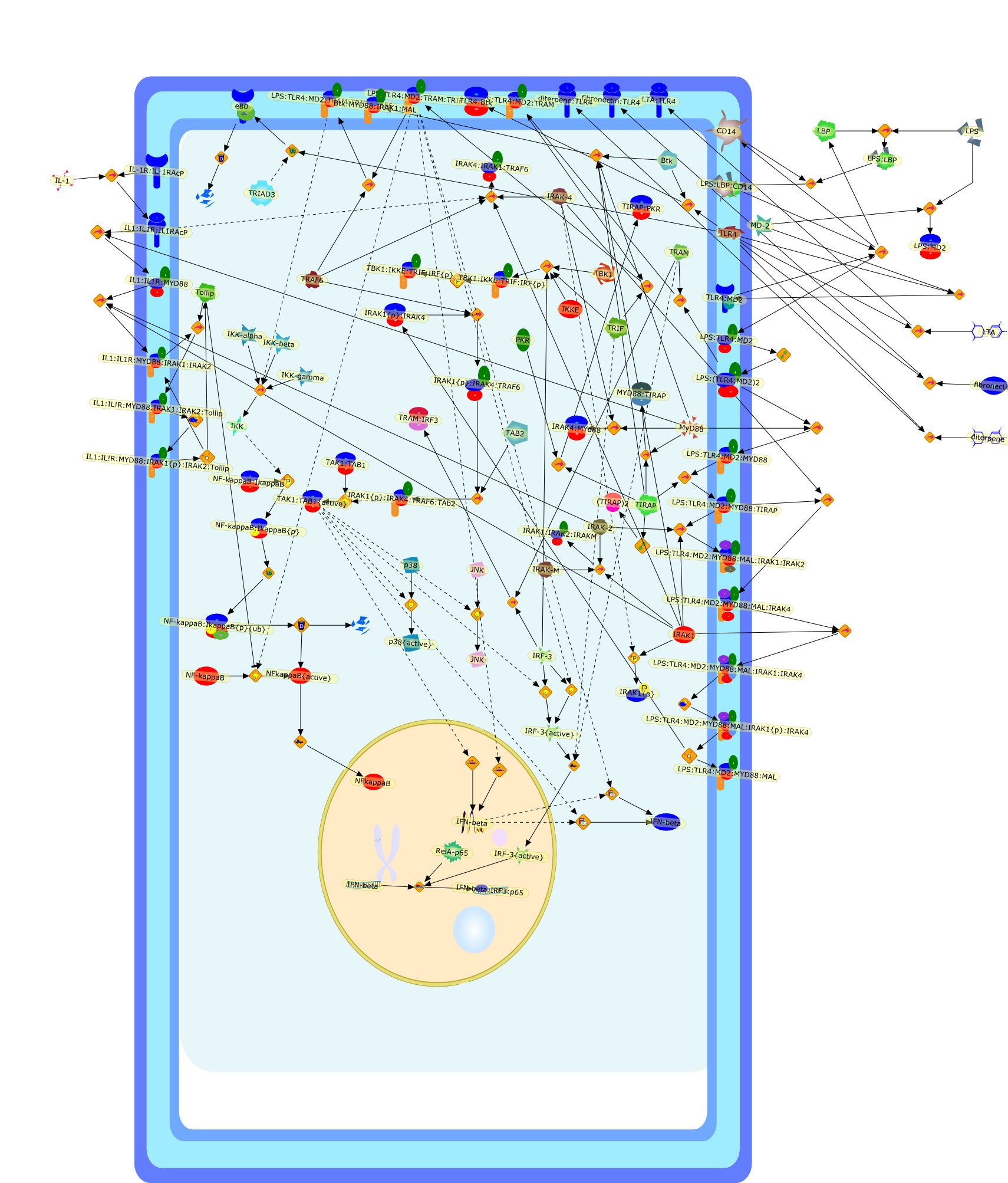
An understanding of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) signal transduction is a key goalin the effort to provide a molecular basis for the lethal effect of LPS duringseptic shock and point the way to novel therapies. Rapid progress in this fieldduring the last 6 years has resulted in the discovery of not only the receptorfor LPS - Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) - but also in a better appreciation of thecomplexity of the signalling pathways activated by LPS. Soon after the discoveryof TLR4, the formation of a receptor complex in response to LPS, consisting ofdimerized TLR4 and MD-2, was described. Intracellular events following theformation of this receptor complex depend on different sets of adapters. Anearly response, which is dependent on MyD88 and MyD88-like adapter (Mal), leadsto the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). A later response to LPSmakes use of TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-beta (TRIF) andTRIF-related adapter molecule (TRAM), and leads to the late activation ofNF-kappaB and IRF3, and to the induction of cytokines, chemokines, and othertranscription factors. As LPS signal transduction is an area of intense researchand rapid progress, this review is intended to sum up our present understandingof the events following LPS binding to TLR4, and we also attempt to create amodel of the signalling pathways activated by LPS.
PMID
15379975
|