| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Infectious non-self recognition in invertebrates: lessons from Drosophila andother insect models.
Affiliation
UPR 9022 CNRS reponse immunitaire des invertebres, Institut de BiologieMoleculaire et Cellulaire, Universite Louis Pasteur, 15 rue Rene Descartes,67084 Strasbourg, France. j.royet@ibmc.u-strasbg.fr
Abstract
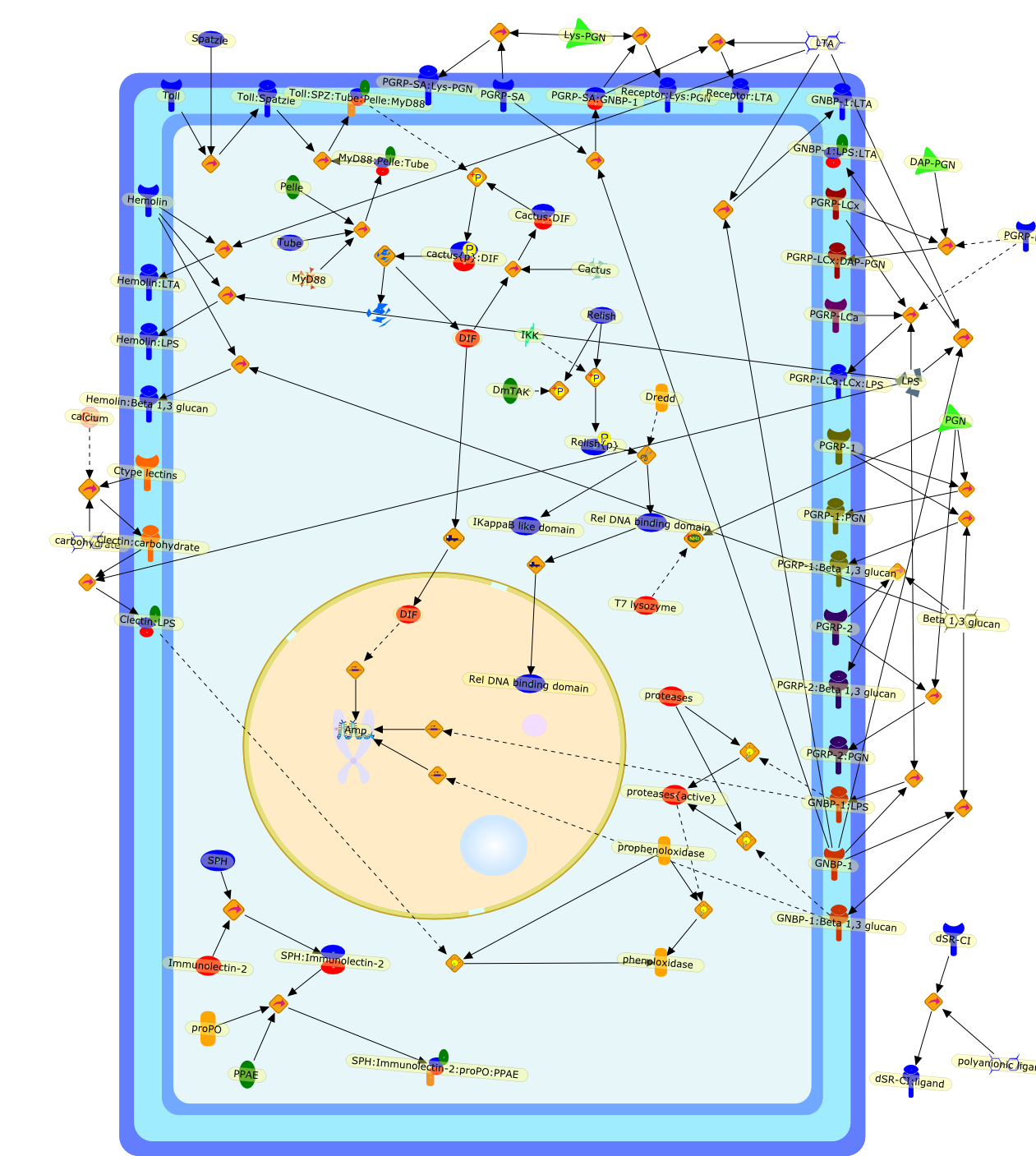
The vertebrate innate immune system recognizes infectious non-self by employinga set of germline-encoded receptors such as nucleotide-binding oligomerisationdomain proteins (NODs) or Toll-like receptors (TLRs). These proteins areinvolved in the recognition of various microbial-derived molecules, includinglipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN) and beta1,3-glucan. DrosophilaToll receptors are not directly dedicated to non-self recognition and insect NODorthologues have not yet been identified. Studies started more than 20 years agoand conducted on different insect models have identified other receptors onwhich invertebrate innate systems rely to sense invading microorganisms.
PMID
15476918
|