| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
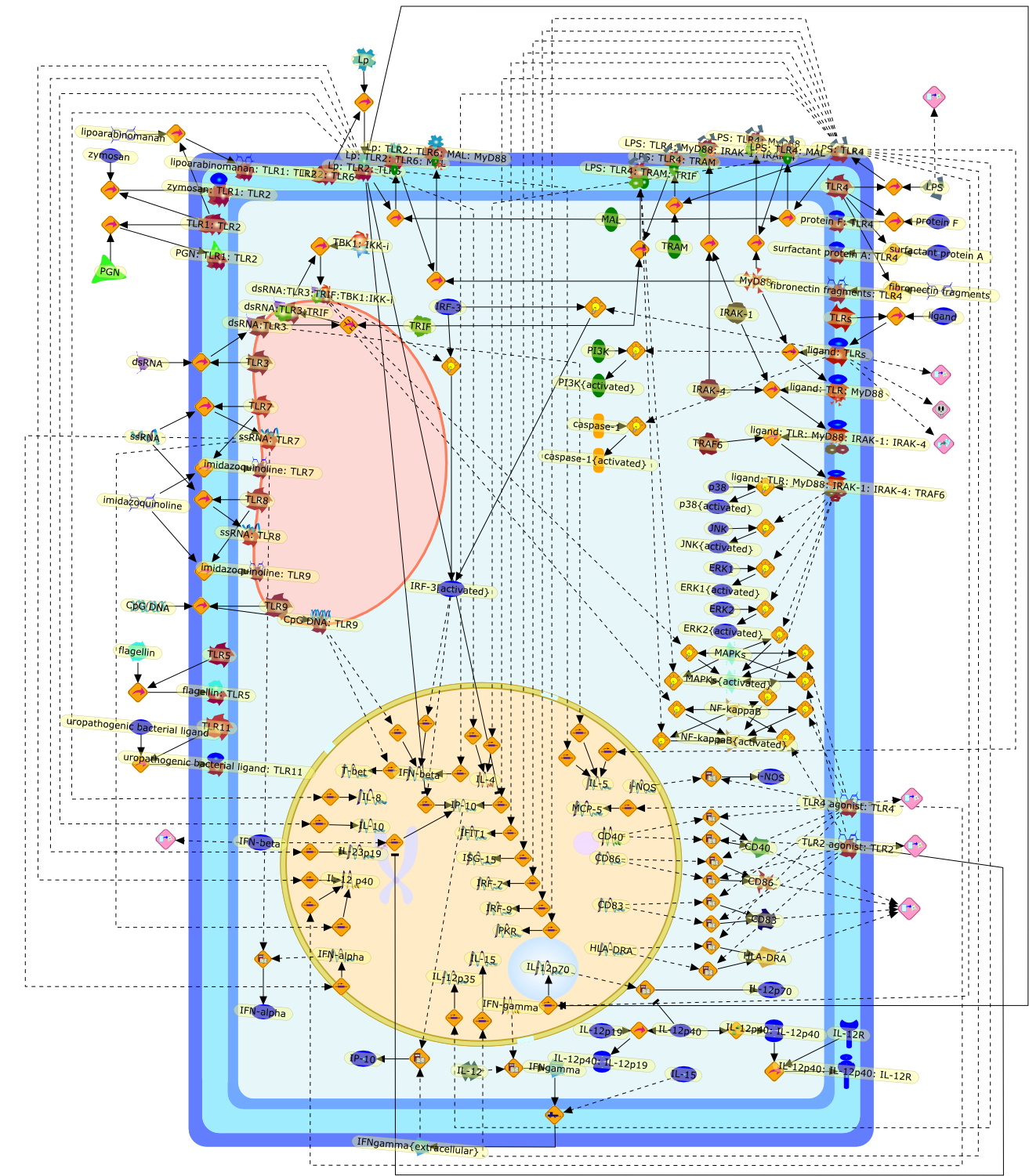
Heterogeneity of TLR-induced responses in dendritic cells: from innate toadaptive immunity.
Affiliation
Department of Cancer Immunology and AIDS, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston,MA 02115, USA. fre@utmem.edu
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLR) mediate recognition of several microbial products.Accumulating evidence indicates that TLR are capable of inducing distinctresponses in dendritic cells and other antigen-presenting cells, and can directT-helper cell differentiation in opposing directions. The generation of suchvaried responses is achieved through the selective utilization of adaptormolecules that link TLR to distinct signal transduction pathways. The ability ofTLR to activate and guide innate and adaptive immunity has the potential to beexploited for practical application that may lead to the development of moresuccessful immunotherapies and vaccination strategies. A review of recentliterature, unpublished observations, and future challenges is presented here.
PMID
15481153
|