| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
LPS, TLR4 and infectious disease diversity.
Affiliation
Department of Medicine, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle,Washington 98195, USA. millersi@u.washington.edu
Abstract
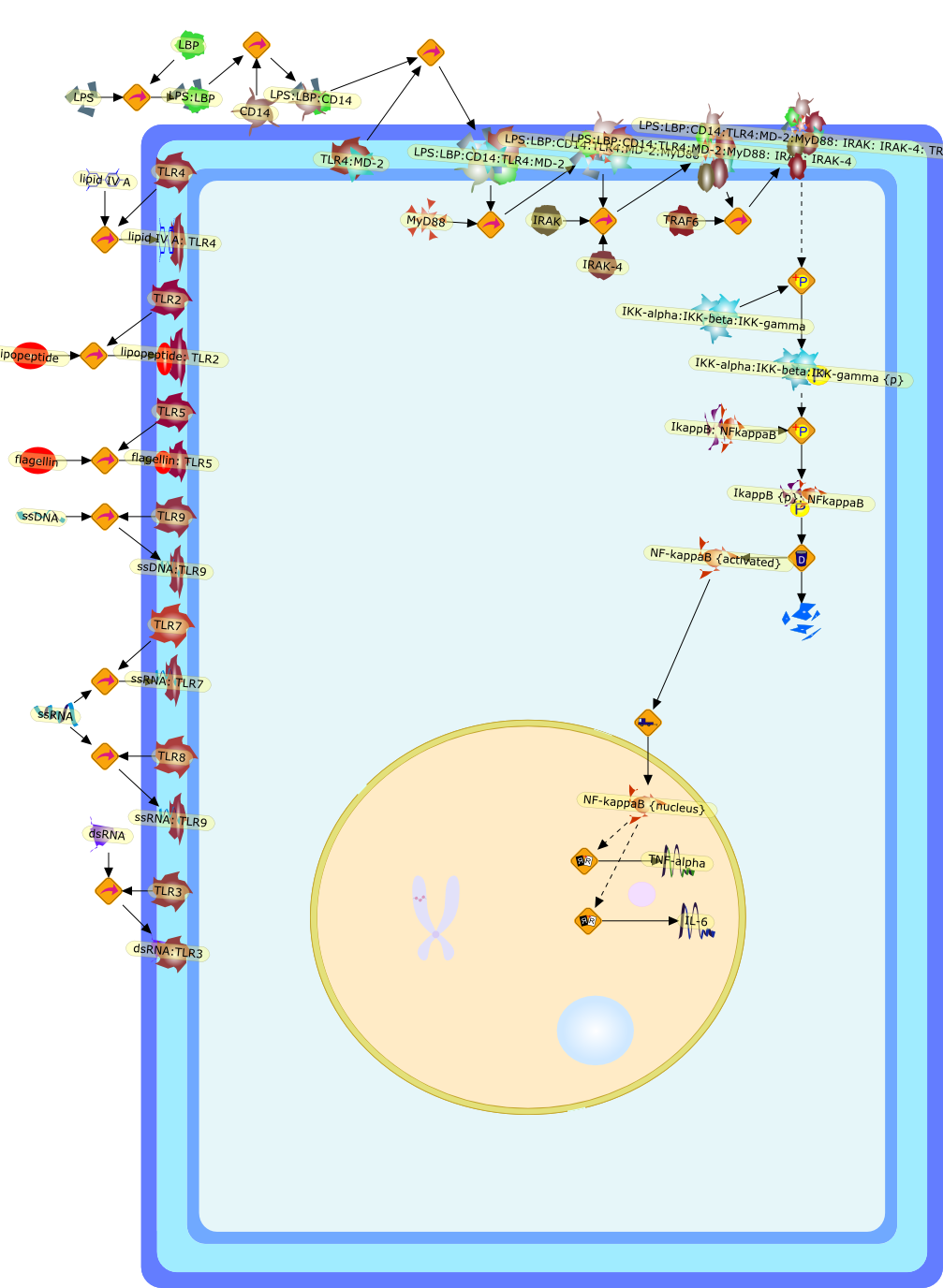
Innate immune receptors recognize microorganism-specific motifs. One suchreceptor-ligand complex is formed between the mammalian Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4)-MD2-CD14 complex and bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Recent researchindicates that there is significant phylogenetic and individual diversity inTLR4-mediated responses. In addition, the diversity of LPS structures and thedifferential recognition of these structures by TLR4 have been associated withseveral bacterial diseases. This review will examine the hypothesis that thevariability of bacterial ligands such as LPS and their innate immune receptorsis an important factor in determining the outcome of infectious disease.
PMID
15608698
|