| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
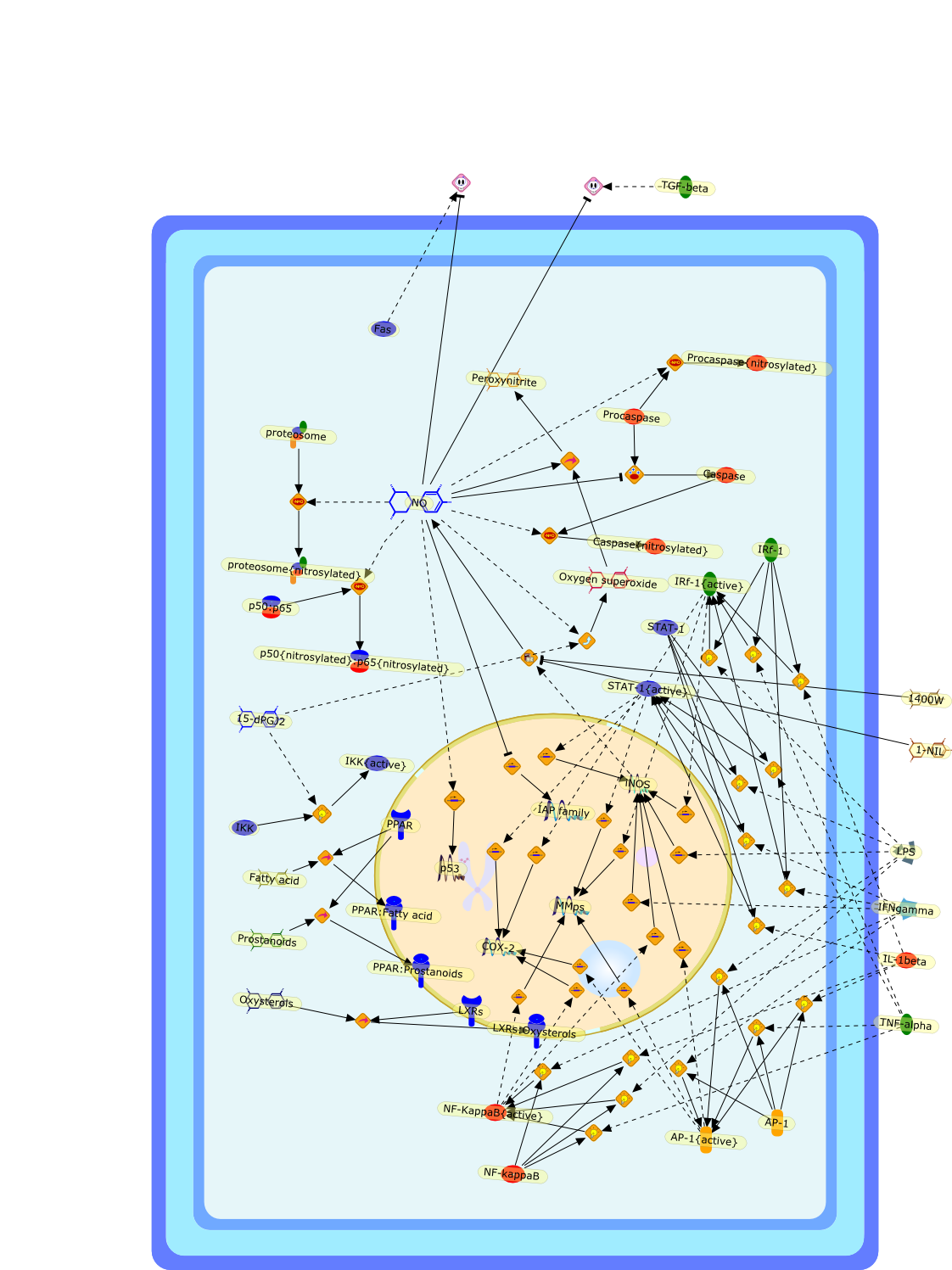
Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: a role for NO inmacrophage function and fate.
Affiliation
Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares, Ronda de Poniente 5, TresCantos, 28760 Madrid, Spain. lbosca@cnic.es
Abstract
Macrophages participate actively in the inflammatory response by releasingcytokines, chemokines and factors that recruit additional cells to sites ofinfection or tissue injury or alteration. In addition to this, activatedmacrophages rapidly activate the expression of genes responsible for thehigh-output synthesis of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (NO, O2-, H2O2 andperoxynitrite, among others) and bioactive lipids derived from arachidonic acid.All of these agents contribute to the regulation of the inflammatory response.Most of these molecules, when synthesized at these high concentrations, exertpro-apoptotic effects in many cell types. Macrophages themselves are a notableand important exception, being resistant to apoptotic death upon activation.This resistance is necessary to enable these cells to perform their functionalrole during the early phases of an inflammatory response. However, aftercumulative damage, or when the synthesis of inflammatory mediators decreases,macrophages undergo the characteristic mitochondrial-dependent cell deathprogram, contributing in this way to the resolution of the inflammatoryreaction. In the case of infectious diseases, this also helps to prevent thedevelopment of parasitic strategies by phagocytosed pathogens.
PMID
15691589
|