| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors. II. Distribution and pathways involved in TLR signalling.
Affiliation
Department of Immunology, Comenius University School of Medicine, Bratislava,Slovakia.
Abstract
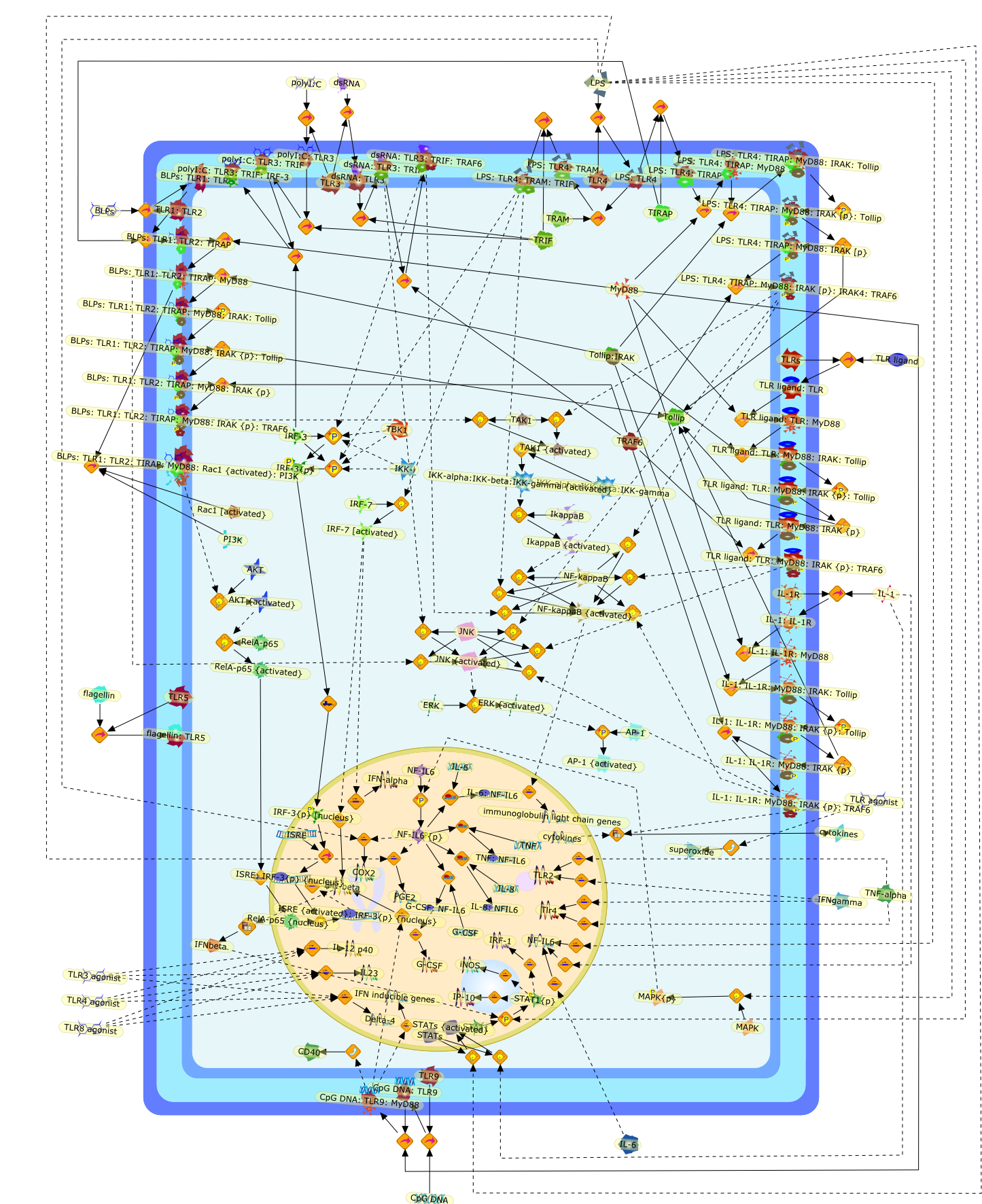
The innate immune system senses invading microorganisms by a phylogeneticallyconserved family of proteins--TLRs. They are expressed in several types of cellsthat represent a route of entry of pathogens into the host organism and that cancontribute to protection against infection. Except for cells of the immunesystem, TLRs are present in epithelial cells of the skin, respiratory,intestinal, and genitourinary tracts that form the first protective barrier toinvading pathogens. Polarized regulation of TLR expression in epithelial cellsexplains why pathogenic but not commensal bacteria elicit inflammatoryresponses. TLR-induced intracellular signalling pathways show remarkablecomplexity: apart from a common signalling pathway, additional signallingpathways specific for each of the TLRs are responsible for a fine tuning of theimmune response, thus securing effective pathogen-directed biological responses.
PMID
16419614
|