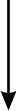| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
All is not Toll: new pathways in DNA recognition.
Affiliation
Institute of Medical Microbiology, Munchen, Germany. h.wagner@lrz.tu-muenchen.de
Abstract
Immunological defense depends on the ability of the innate immune system torecognize invading microbes as foreign and thus eliminate them. The Toll-likereceptors (TLRs) help detect foreign invaders by sensing variouspathogen-associated molecules, including microbial RNA and DNA. At present, itis unclear whether and how the immune system distinguishes between microbial andself nucleic acids, as host-derived RNA and DNA also stimulate TLRs. Inaddition, recent studies have revealed the existence of TLR-independent pathwaysthat are activated in response to microbial and host nucleic acids.
PMID
16446382
|