| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
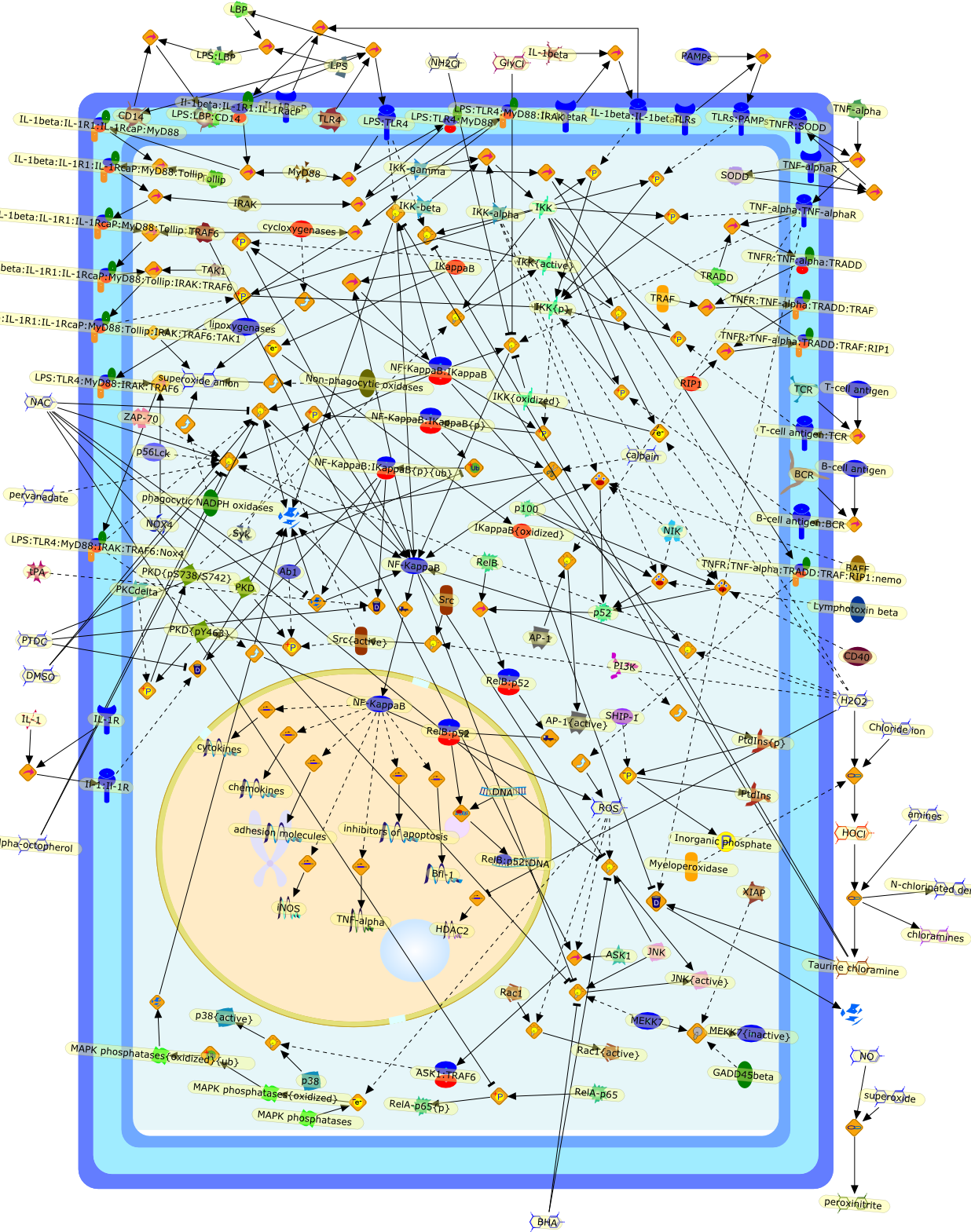
NF-kappaB activation by reactive oxygen species: fifteen years later.
Affiliation
Center for Biomedical Integrated Genoproteomics (CBIG), Virology and ImmunologyUnit, University of Liege, 4000 Liege, Belgium.
Abstract
The transcription factor NF-kappaB plays a major role in coordinating innate andadaptative immunity, cellular proliferation, apoptosis and development. Sincethe discovery in 1991 that NF-kappaB may be activated by H(2)O(2), severallaboratories have put a considerable effort into dissecting the molecularmechanisms underlying this activation. Whereas early studies revealed anatypical mechanism of activation, leading to IkappaBalpha Y42 phosphorylationindependently of IkappaB kinase (IKK), recent findings suggest that H(2)O(2)activates NF-kappaB mainly through the classical IKK-dependent pathway. Themolecular mechanisms leading to IKK activation are, however, cell-type specificand will be presented here. In this review, we also describe the effect of otherROS (HOCl and (1)O(2)) and reactive nitrogen species on NF-kappaB activation.Finally, we critically review the recent data highlighting the role of ROS inNF-kappaB activation by proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha and IL-1beta) andlipopolysaccharide (LPS), two major components of innate immunity.
PMID
16723122
|