| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Innate immune responses: crosstalk of signaling and regulation of genetranscription.
Affiliation
College of Life Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China.
Abstract
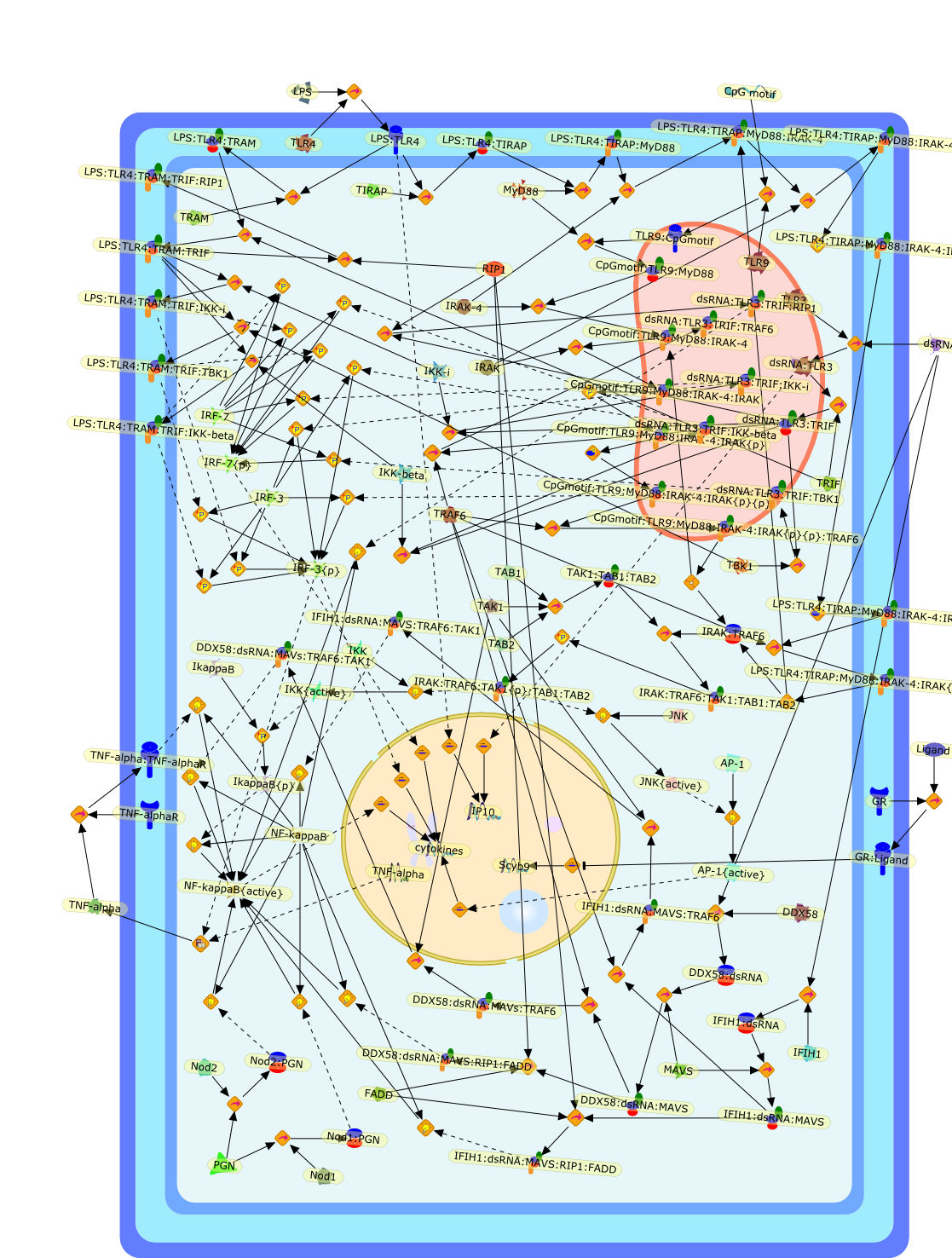
Innate immune responses to pathogens such as bacteria and viruses are triggeredby recognition of specific structures of invading pathogens calledpathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by cellular pattern recognitionreceptors (PRRs) that are located at plasma membrane or inside cells.Stimulation of different PAMPs activates Toll-like receptor (TLR)-dependent and-independent signaling pathways that lead to activation of transcription factorsnuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), interferon regulatory factor 3/7 (IRF3/7)and/or activator protein-1 (AP-1), which collaborate to induce transcription ofa large number of downstream genes. This review focuses on the rapid progressthat has recently improved our understanding of the crosstalk among the pathwaysand the precise regulation of transcription of the downstream genes.
PMID
16753195
|