| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors and RNA helicases: two parallel ways to trigger antiviralresponses.
Affiliation
Department of Biochemistry, University of Lausanne, BIL Biomedical ResearchCenter, Chemin des Boveresses 155, CH-1066 Epalinges, Switzerland.
Abstract
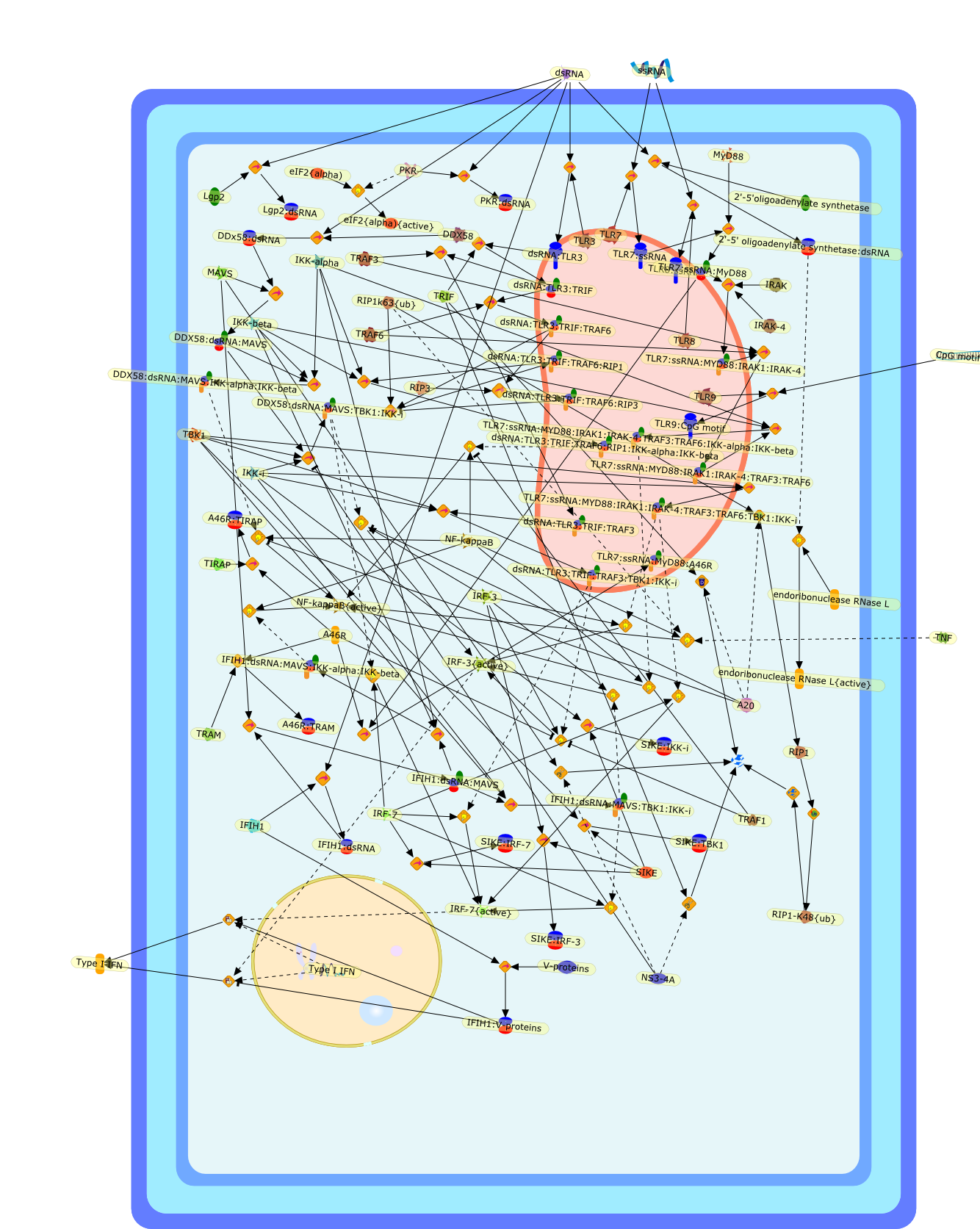
The early detection by the host of invading microorganisms, including viruses,depends on a limited number of specific receptors that recognizepathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). A few of these PAMPs, includingssRNA and dsRNA, are recognized by Toll-like receptors (TLR)-7/8 and TLR3,respectively. Activation of an antiviral TLR-dependent signaling cascade leadsto the activation of the key transcription factors IRF and NF-kappaB, whichpromote antiviral responses through induction of specific genes. Recently, asecond system has been described, which relies on the cytoplasmic recognition ofdsRNA by RNA helicases such as RIG-I. In this review, we discuss the mechanisticaspects of these important arms of the host innate response to dsRNA and a fewviral strategies utilized to counteract them.
PMID
16762830
|