| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
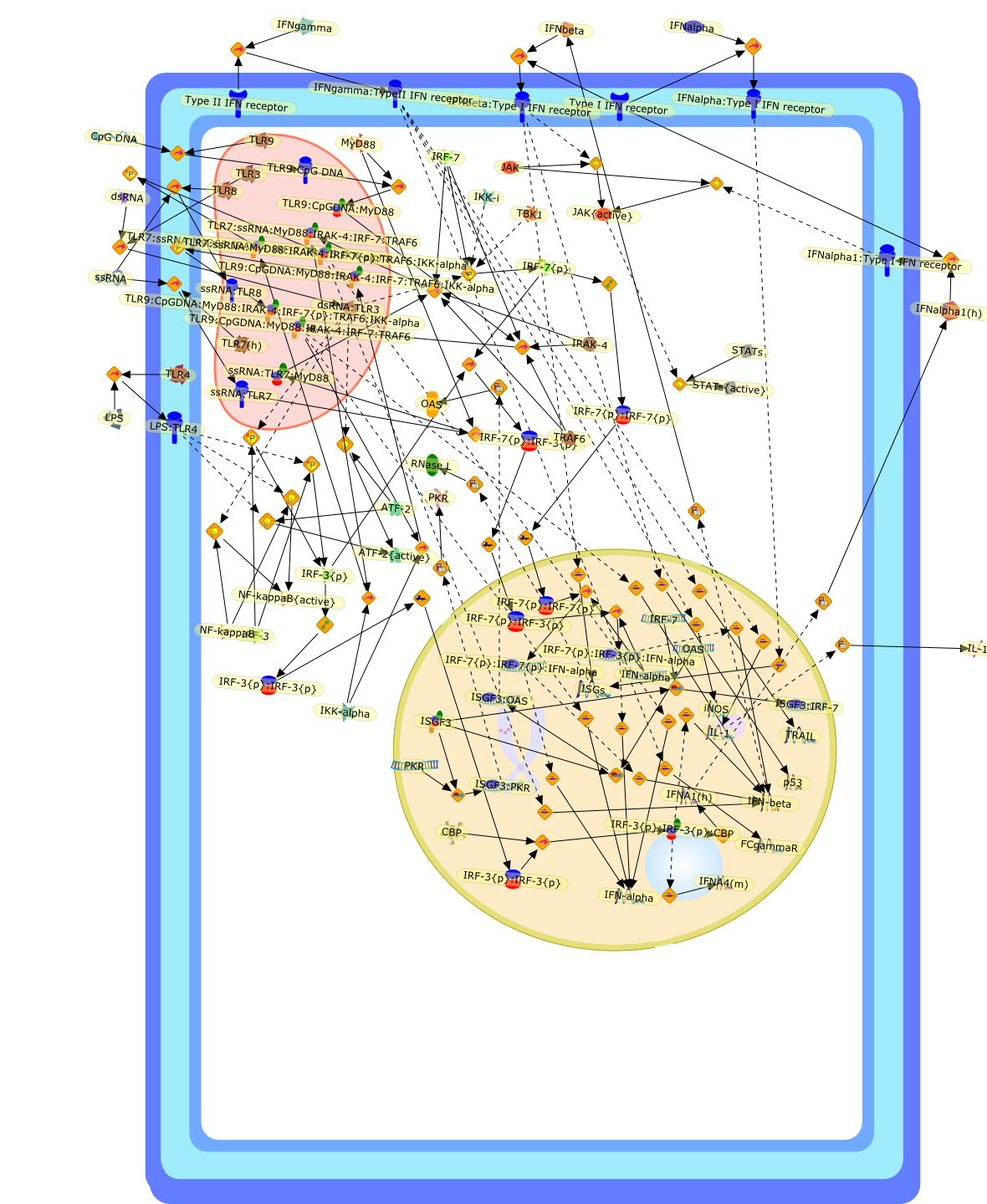
Distinct functions of IRF-3 and IRF-7 in IFN-alpha gene regulation and controlof anti-tumor activity in primary macrophages.
Affiliation
Terry Fox Molecular Oncology Group, Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research,McGill University, Montreal, Canada H3T 1E2.
Abstract
Type I IFN (IFN-alpha/beta) have important biological functions ranging fromimmune cell development and activation, to tumor cell killing and mostimportantly inhibition of virus replication. Following viral infection oractivation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) via distinct ligands, IFN-alpha/betaare produced. Two members of the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) family -IRF-3 and IRF-7 - are the major modulators of IFN gene expression. Activation ofIRF-3 and IRF-7 by TBK1/IKKvarepsilon mediated phosphorylation promotes IFN geneexpression and potentiates the production of IFN responsive genes important tothe development of an effective antiviral immune response. IFN treatment canaugment anti-tumor properties and they are potentially key players in cancertherapy. For example, adoptive transfer of IFN-gamma-activated macrophages canmediate tumor cell killing via direct cell-cell contact, as well as release ofsoluble cytotoxic pro-inflammatory molecules. A recent study investigatedwhether IRF-3 and IRF-7 could mediate the acquisition of new anti-tumor effectorfunctions in macrophages. Adenovirus mediated transduction of the active form ofIRF-7 into primary macrophages resulted in the production of type I IFN,upregulation of target genes including TRAIL and increased tumoricidal activityof macrophages; in contrast, the active form of IRF-3 led to induction of celldeath. These studies indicate that IRF-7 transduced macrophages may be anattractive candidate for in vivo adoptive therapy of cancer.
PMID
16846591
|