| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
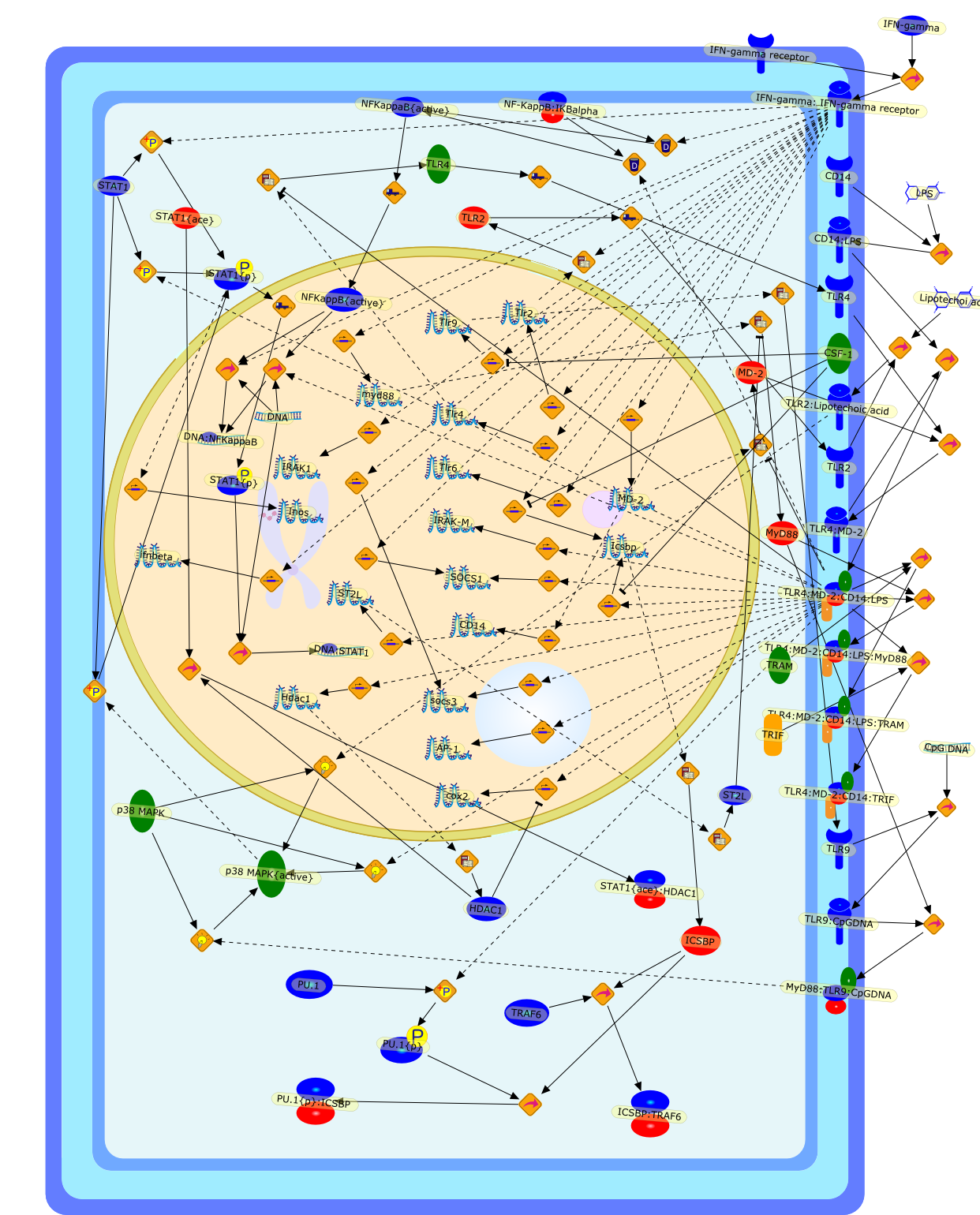
Signal integration between IFNgamma and TLR signalling pathways in macrophages.
Affiliation
Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University of Queensland, QLD BiosciencePrecinct, Brisbane, QLD 4072, Australia. K.Schroder@imb.uq.edu.au
Abstract
Macrophages are major effector cells of the innate immune system, andappropriate regulation of macrophage function requires the integration ofmultiple signalling inputs derived from the recognition of host factors (e.g.interferon-gamma/IFNgamma) and pathogen products (e.g. toll-like receptor/TLRagonists). The profound effects of IFNgamma pre-treatment ("priming") onTLR-induced macrophage activation have long been recognised, but many of themechanisms underlying the priming phenotype have only recently been identified.This review summarises the known mechanisms of integration between the IFNgammaand TLR signalling pathways. Synergy occurs at multiple levels, ranging fromsignal recognition to convergence of signals at the promoters of target genes.In particular, the cross-talk between the IFNgamma, and LPS and CpG DNAsignalling pathways is discussed.
PMID
16920490
|