| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights intotranscriptional regulations in innate immunity.
Affiliation
School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2,Ireland. doylesl@tcd.ie
Abstract
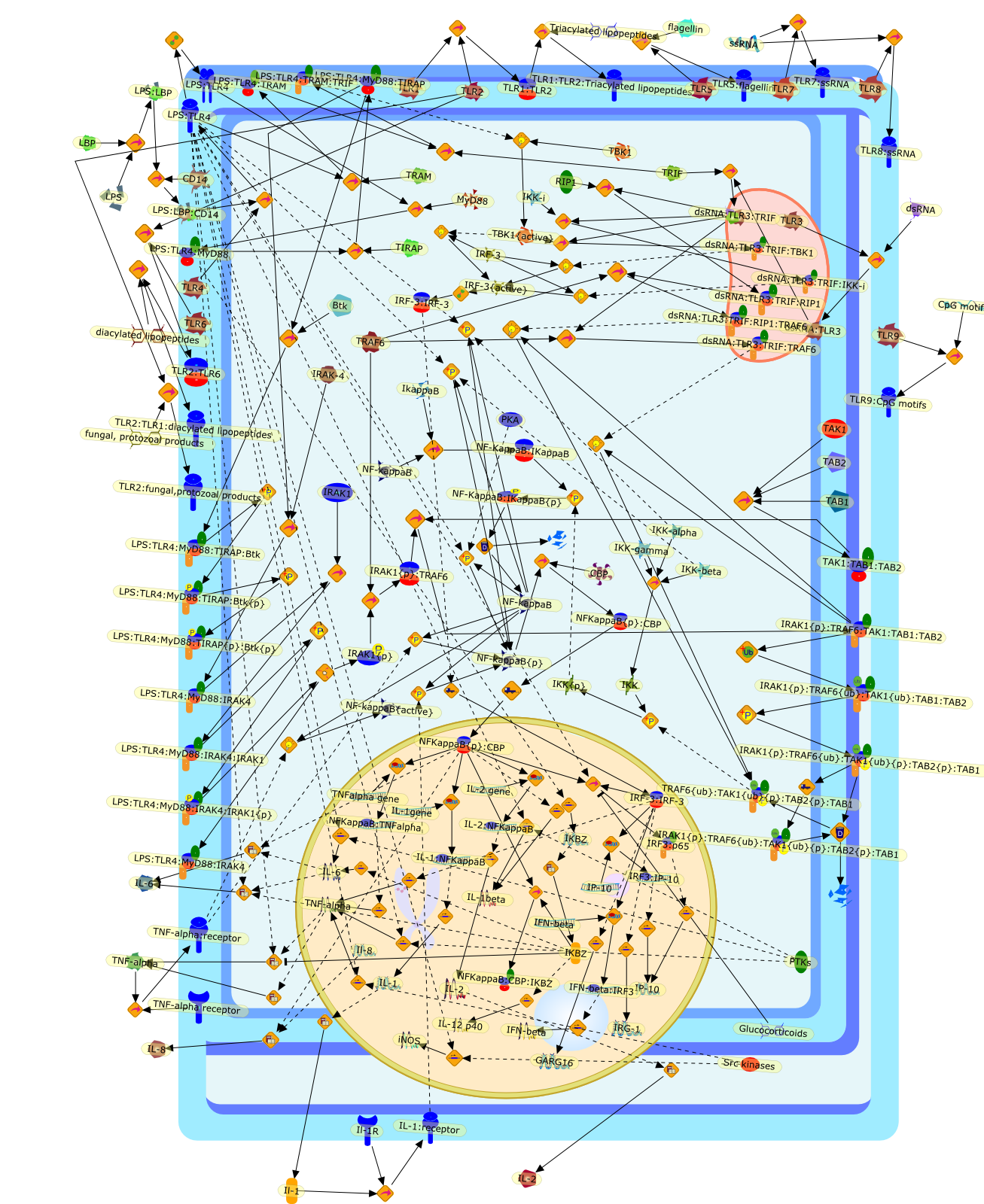
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are key components of the innate immune system,functioning as pattern recognition receptors that recognise a wide range ofmicrobial pathogens. TLRs represent a primary line of defence against invadingpathogens in mammals, plants and insects. Recognition of microbial components byTLRs triggers a cascade of cellular signals that culminates in the activation ofNFkappaB which leads to inflammatory gene expression and clearance of theinfectious agent. The history of NFkappaB began with the TLR4 ligandlipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component of the cell wall of Gram-negativebacteria, since this was the stimulus first used to activate NFkappaB inpre-B-cells. However, since those early days it has been a circuitous route,made possible by drawing on information provided by many different fields, thathas led us not only to the discovery of TLRs but also to an understanding of thecomplex pathways that lead from TLR ligation to NFkappaB activation. In thisreview we will summarize the current knowledge of TLR-mediated NFkappaBactivation, and also the recent discoveries that subtle differences in kappaBbinding sequences and NFkappaB dimer formation result in specific geneexpression profiles.
PMID
16930560
|