| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
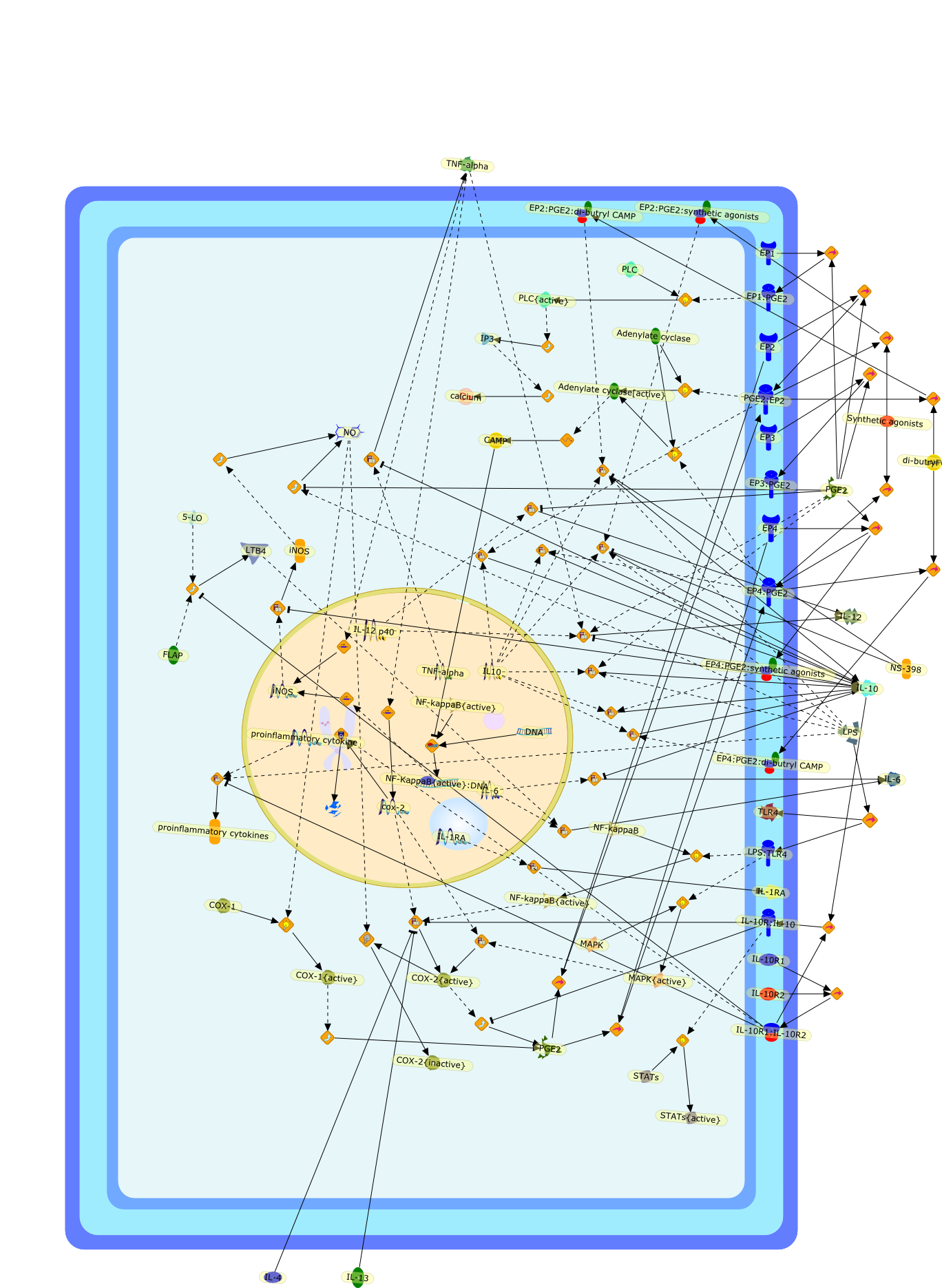
Pivotal role of PGE2 and IL-10 in the cross-regulation of dendritic cell-derivedinflammatory mediators.
Affiliation
CNRS UMR 5540, Bordeaux, Universite Bordeaux 2, France. harizihedi33@yahoo.fr
Abstract
Exposure to pathogens induces antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as macrophagesand dendritic cells (DC) to produce various endogenous mediators, includingarachidonic acid (AA)-derived eicosanoids, cytokines, and nitric oxide (NO).Many secreted products of activated APC can act by themselves in an autocrinemanner and modulate their function. Moreover, the cross-interaction betweenendogenous bioactive molecules regulates the function of professional APC withimportant consequences for their ability to activate and sustain immune andinflammatory responses, and to regulate immune homeostasis. Although neglectedfor many years when compared to their role in cardiovascular homeostasis, cancerand inflammation, the importance of eicosanoids in immunology is becoming moredefined. The role of prostaglandin (PG) E2 (PGE2), one of the best known andmost well studied eicosanoids, is of particular interest. It modulates theactivities of professional DC by acting on their differentiation, maturation andtheir ability to secrete cytokines. Uniquely among haematopoietic cytokines,interleukin-10 (IL-10) is a pleiotropic molecule that displays bothimmunostimulatory and immunoregulatory activities. IL-10 has attached muchattention because of its anti-inflammatory properties. It modulates expressionof cytokines, soluble mediators and cell surface molecules by cells of myeloidorigin, particularly macrophages and DC. We previously reported that PGE2 is apotent inducer of IL-10 in bone marrow-derived DC (BM-DC), and PGE2-inducedIL-10 is a key regulator of the BM-DC pro-inflammatory phenotype. BM-DC may beconsidered as an important model to study complex interactions betweenendogenous mediators, and autocrine IL-10 plays a pivotal role in thecrossregulation of AA-derived lipid mediators, cytokines, and NO, with criticaleffects on immune and inflammatory responses.
PMID
16978535
|