| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Fifty years of interferon research: aiming at a moving target.
Affiliation
Department of Microbiology, New York University School of Medicine, New York,New York 10016, USA. jan.vilcek@med.nyu.edu
Abstract
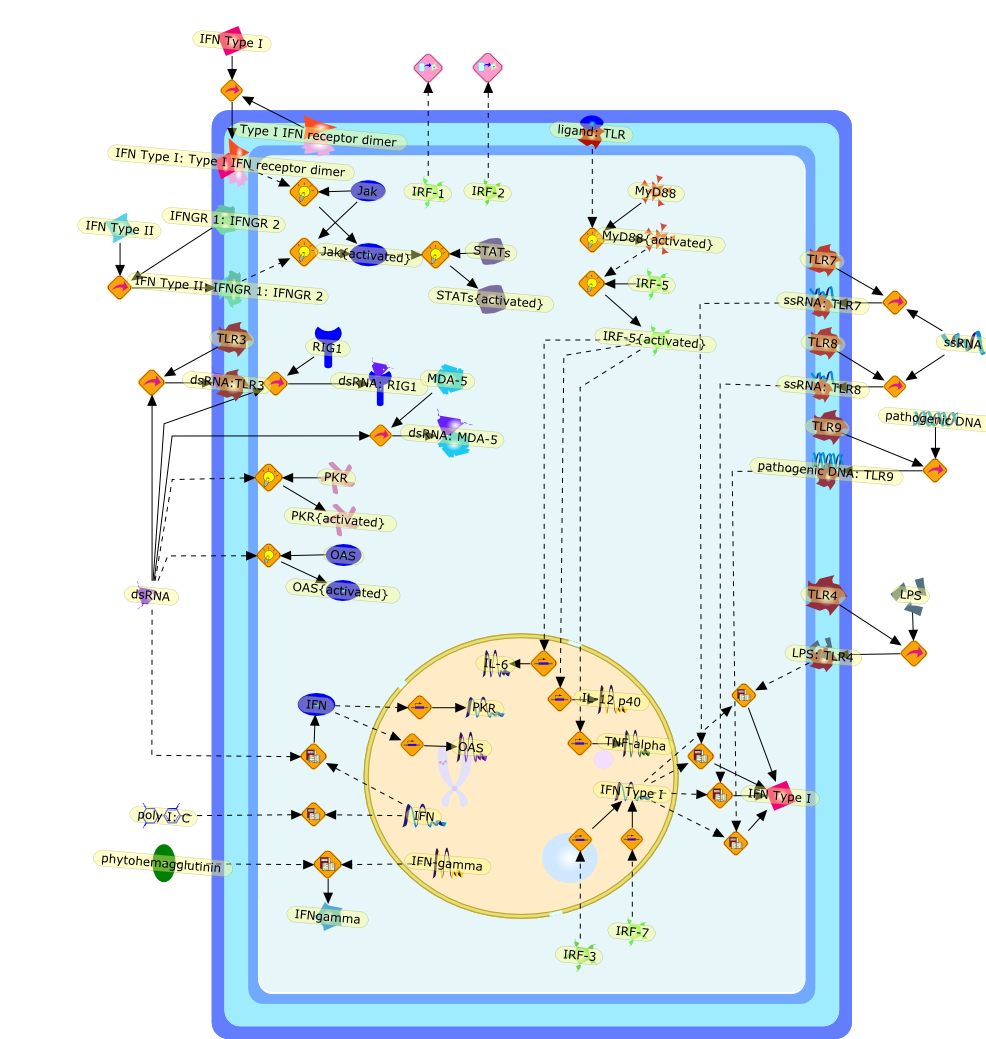
Nearly half a century has passed since the first published description ofinterferons (IFNs). This commentary introduces the four accompanying reviewarticles on type I IFN research and attempts to relate how the field of IFNresearch has been changing during its history.
PMID
16979566
|