| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factorfamily of transcription factors.
Affiliation
Department of Immunology, Graduate School of Medicine and Faculty of Medicine,University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.
Abstract
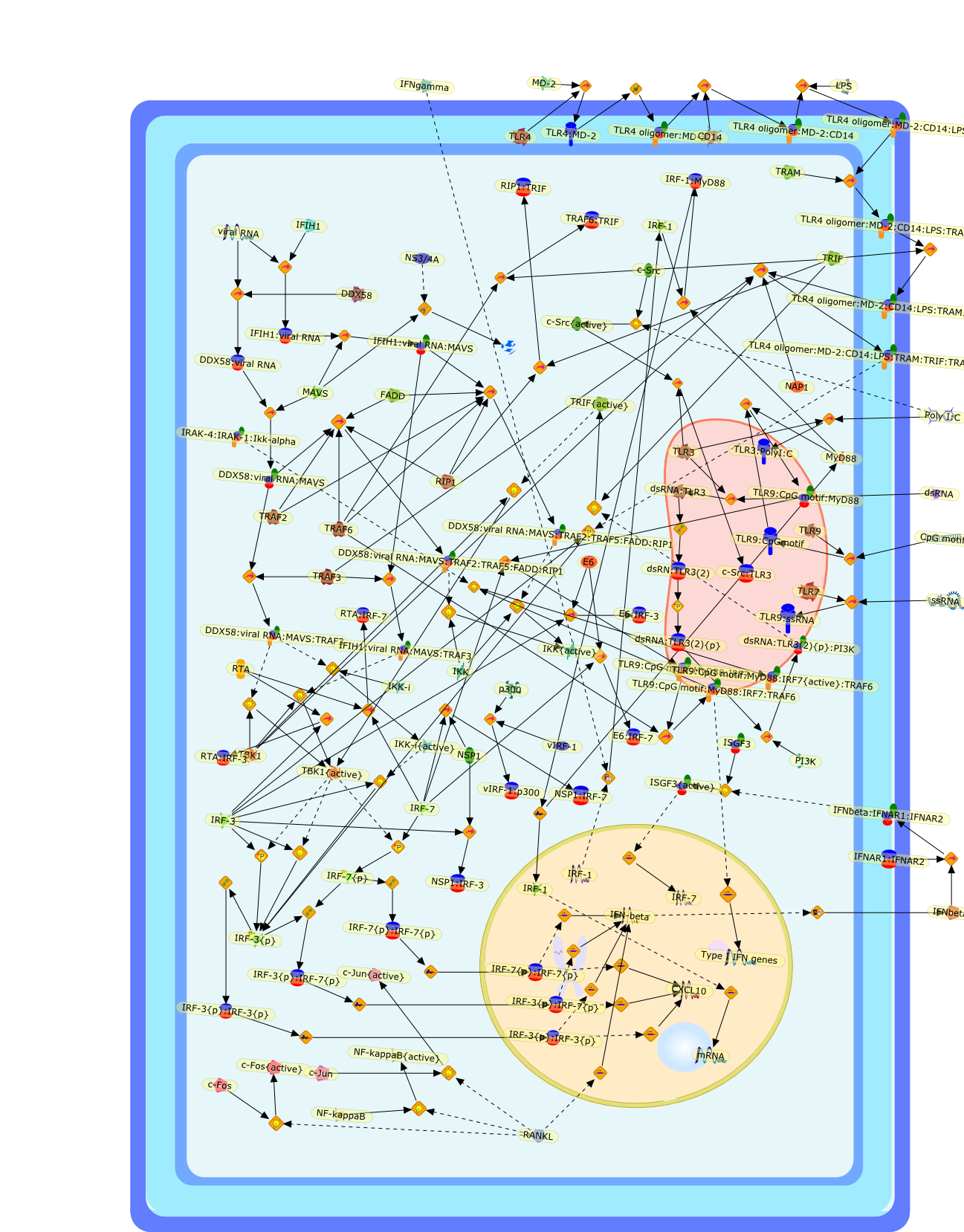
Induction of type I interferons (IFNs) by viruses and other pathogens is crucialfor innate immunity, and it is mediated by the activation of pattern-recognitionreceptors, such as Toll-like receptors and cytosolic receptors such as RIG-I andMDA5. The type I IFN induction is primarily controlled at the genetranscriptional level, wherein a family of transcription factors, interferonregulatory factors (IRFs), plays central roles. Here, we summarize the recentstudies on IRFs, providing a paradigm of how genes are ingeniously regulatedduring immune responses. We also consider some evolutional aspects on theIFN-IRF system.
PMID
16979567
|