| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Ubiquitin: tool and target for intracellular NF-kappaB inhibitors.
Affiliation
Unit of Molecular Signal Transduction in Inflammation, Department for MolecularBiomedical Research, Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB)- Ghent University, Technologiepark 927, B-9052 Ghent (Zwijnaarde), Belgium.
Abstract
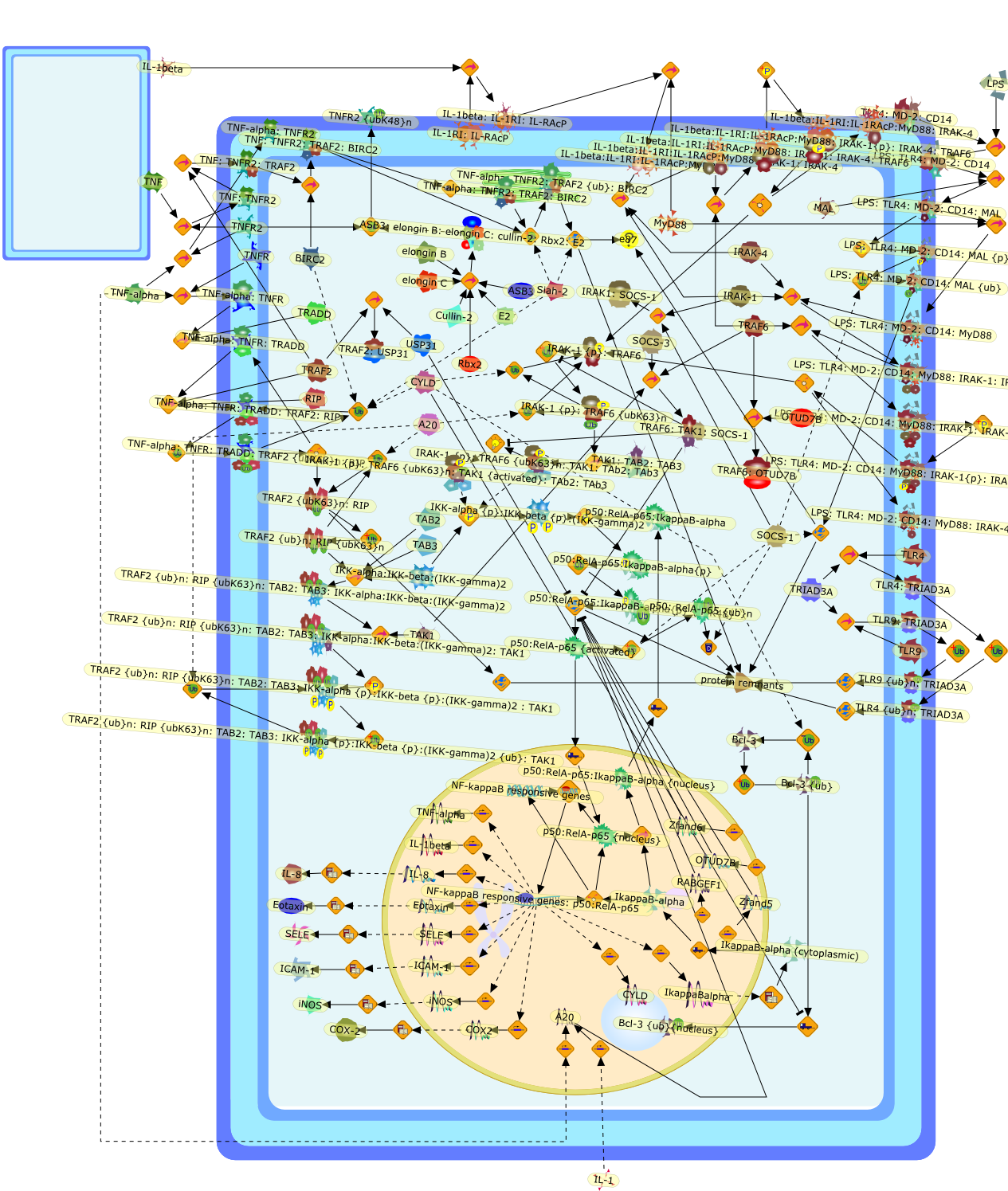
The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) has a pivotal role ininitiating inflammation and raising an effective immune response. BecauseNF-kappaB activation depends on ubiquitination, cells have developed ubiquitin(Ub)-mediated strategies for inhibiting NF-kappaB activation and preventingexcessive inflammation. Recent findings concerning tumor necrosis factor (TNF)receptor and toll-like receptor (TLR)-interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor signallingpathways show that Ub can be a tool as well as a target for NF-kappaB inhibitoryproteins, either by labelling specific signalling proteins forproteasome-dependent degradation or by serving as a target for specificde-ubiquitinating enzymes that prevent the formation of pertinent signallingcomplexes. Interfering with ubiquitination therefore seems to be a versatilemeans for regulating NF-kappaB activity, indicating that studies of Ub-mediatedsignalling might hold the key for developing new therapeutic strategies forinflammatory disease.
PMID
16982211
|