| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
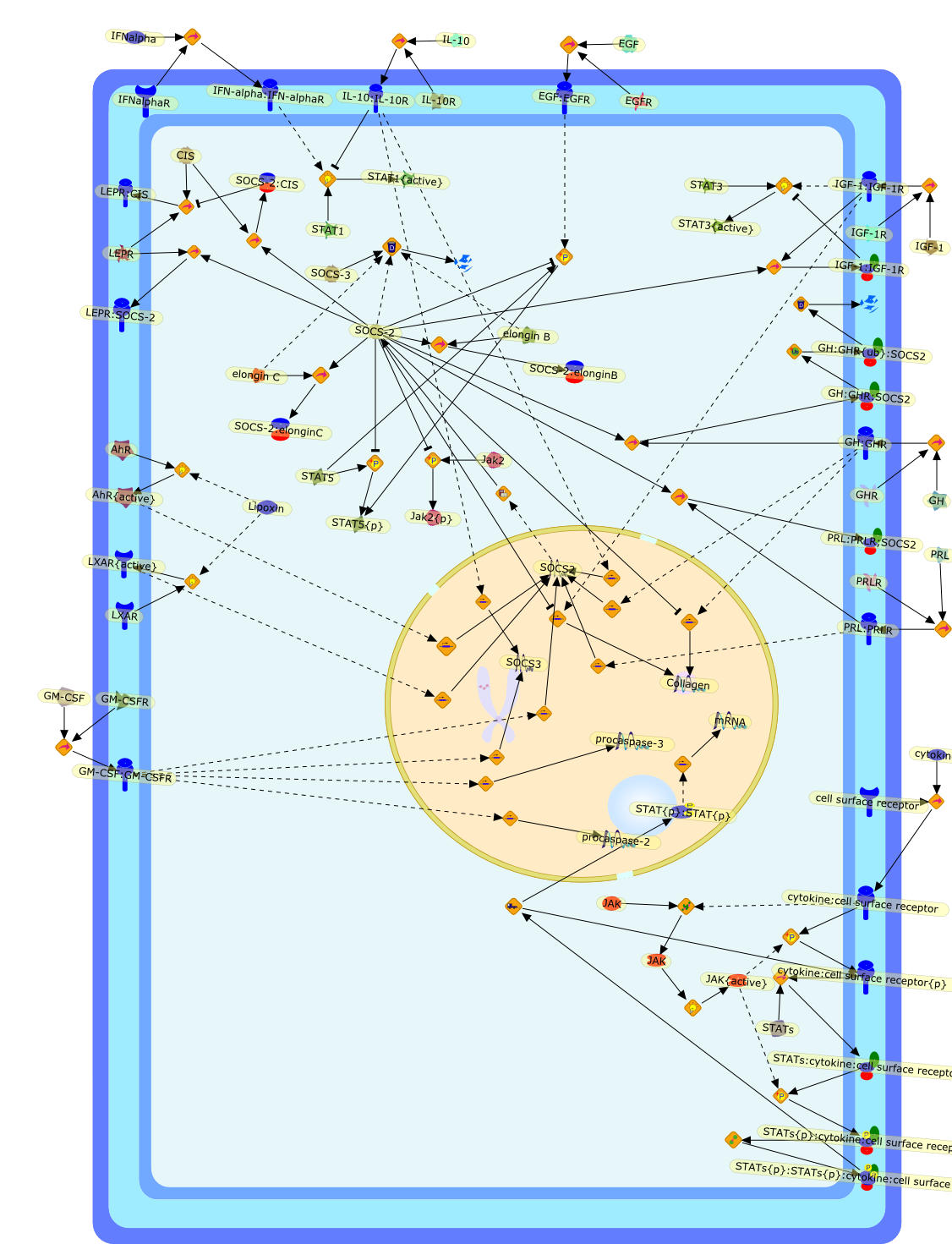
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 2, a protein with multiple functions.
Affiliation
Molecular Endocrinology Group, Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery,Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
Abstract
Cytokine receptors act through a complex signaling network, involving Januskinases (JAKs) and the signal transducers and activators of transcription(STATs), to regulate diverse biological processes which control growth,development, homeostasis and immune function, among others. The JAK/STATsignaling pathway is attenuated via three mechanisms controlling the initiation,magnitude, and duration of the signal: the PIAS proteins, which prevent STATdimerization or DNA interaction, the SHP phosphatases, which dephosphorylateactivating tyrosine phosphorylations, and the suppressors of cytokine signaling(SOCS), which are transcribed in response to cytokine stimulation and useseveral interconnected mechanisms to downregulate the signal. Specific studiestargeting the SOCS genes in vivo have unveiled SOCS2 as the main regulator ofsomatic growth through regulation of GH/IGF-1 signaling. In addition, severalstudies indicate that SOCS2 also has important actions in the central nervoussystem, the regulation of metabolism, the immune response, the mammary glanddevelopment, cancer, and other cytokine-dependent signaling pathways. Consistentwith the role of cytokines in human physiology, any SOCS2 imbalance could resultin a broad range of pathologies such as cardiovascular diseases, insulinresistance, cancer, and severe infections, among others. Thus, determining theimportance of SOCS2 in health and disease will no doubt aid in the developmentof novel therapeutic strategies. In this review, we attempt to summarize theavailable information, including our results, regarding the role of SOCS2 inseveral biological processes.
PMID
17070092
|