| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Nucleic acid-sensing TLRs as modifiers of autoimmunity.
Affiliation
Laboratory of Immunogenetics, National Institute of Allergy and InfectiousDiseases, National Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD 20852, USA.
Abstract
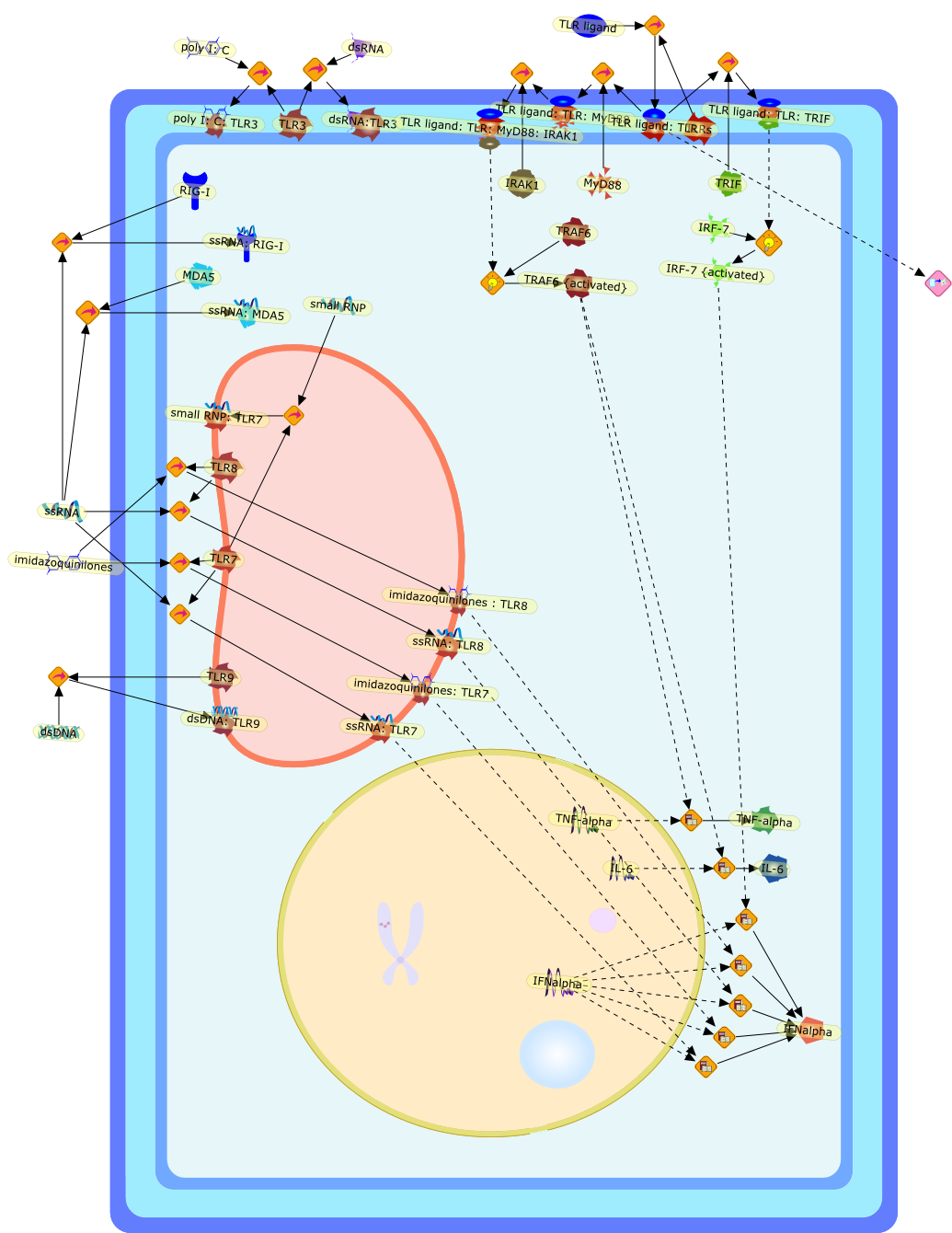
The immune system requires precise regulation of activating and inhibitorysignals so that it can mount effective responses against pathogens whileensuring tolerance to self-components. Some of the most potent activationsignals are triggered by innate immune molecules, particularly those in the TLRfamily. Recent studies have shown that engagement of TLRs plays a significantrole in both innate and adaptive immunity. This review focuses on the ways thatTLR function might contribute to the etiology of lupus-like syndromes in thecontext of an autoimmune-prone environment. By considering the sources,localization, and expression of both nucleic acids and the molecules that bindthem, we discuss several ways that innate immunity can play a role in thedevelopment of systemic autoimmunity.
PMID
17082566
|