| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Endogenous anti-inflammatory substances, inter-alpha-inhibitor and bikunin.
Affiliation
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Nara Medical University, Kashihara,Nara 634-8522, Japan. hirokoba@naramed-u.ac.jp
Abstract
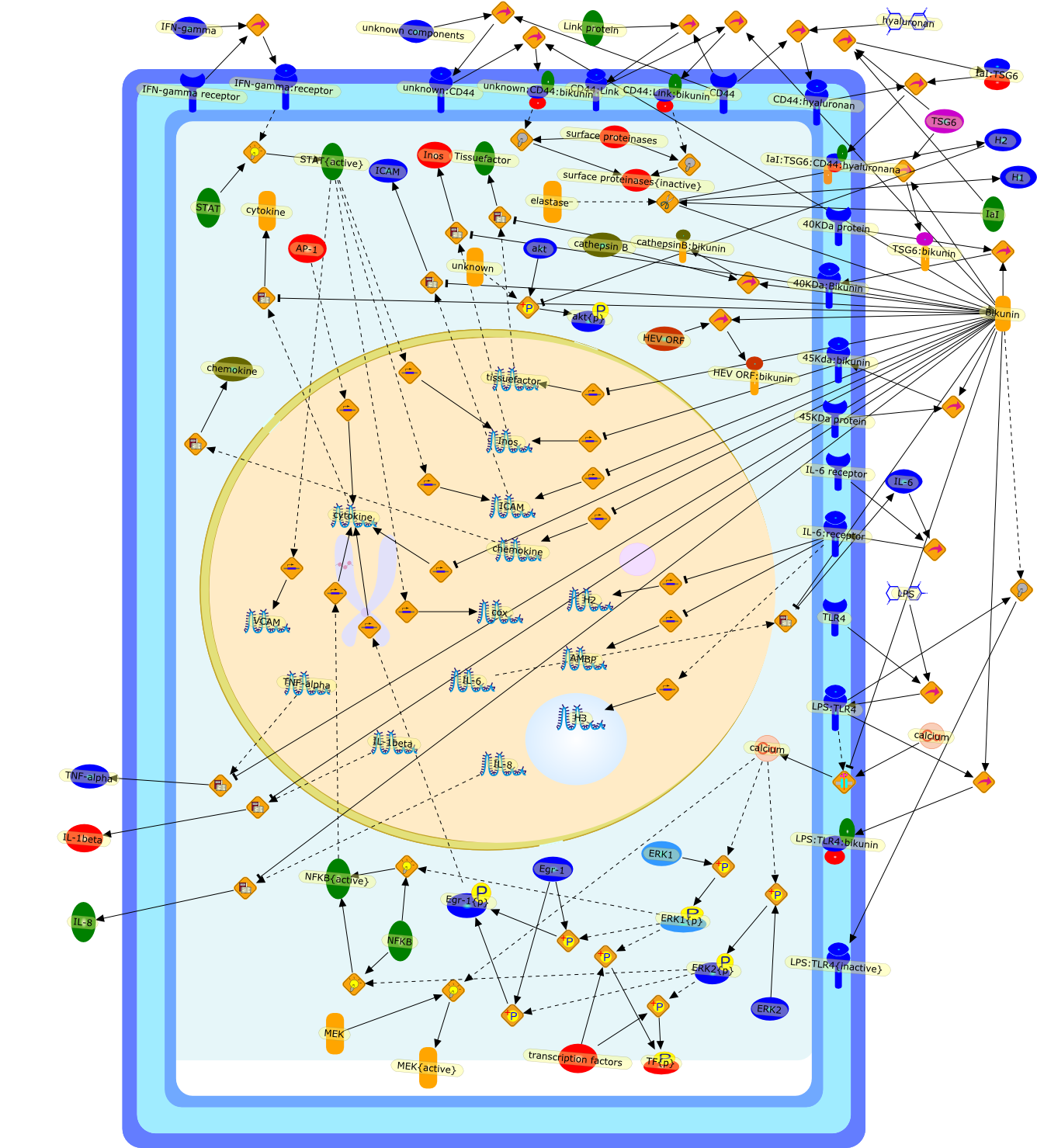
There have been new developments in the elucidation of the biological functionsof the inter-alpha-inhibitor (IalphaI) family. The anti-proteolytic activity ofthe IalphaI family originates from bikunin (also known as urinary trypsininhibitor). Growing evidence indicates that bikunin is not just ananti-proteolytic agent, but can also be considered an anti-inflammatory agentthat suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cytokine synthesis. Bikuninfunctions to inhibit calcium influx and extracellular signal-regulated kinase(ERK) signaling via LPS receptors and/or as yet unidentified bikunin signalingreceptors. By signaling via the LPS receptor, LPS increases calcium influx andyields phosphorylated ERK, which activates multiple transcription factors, suchas nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) or early growth response-1 (Egr-1), whichin turn promote cytokine expression. Deficits in the signaling cascades causedby free or cell-bound bikunin are predicted to down-regulate cytokineexpression, render macrophages/neutrophils more inactive, and impairinflammatory processes. This brief review largely focuses on our currentunderstanding of the apparent functions of bikunin, its ligands, the effectormolecules with which it interacts, and its regulation.
PMID
17132099
|