| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
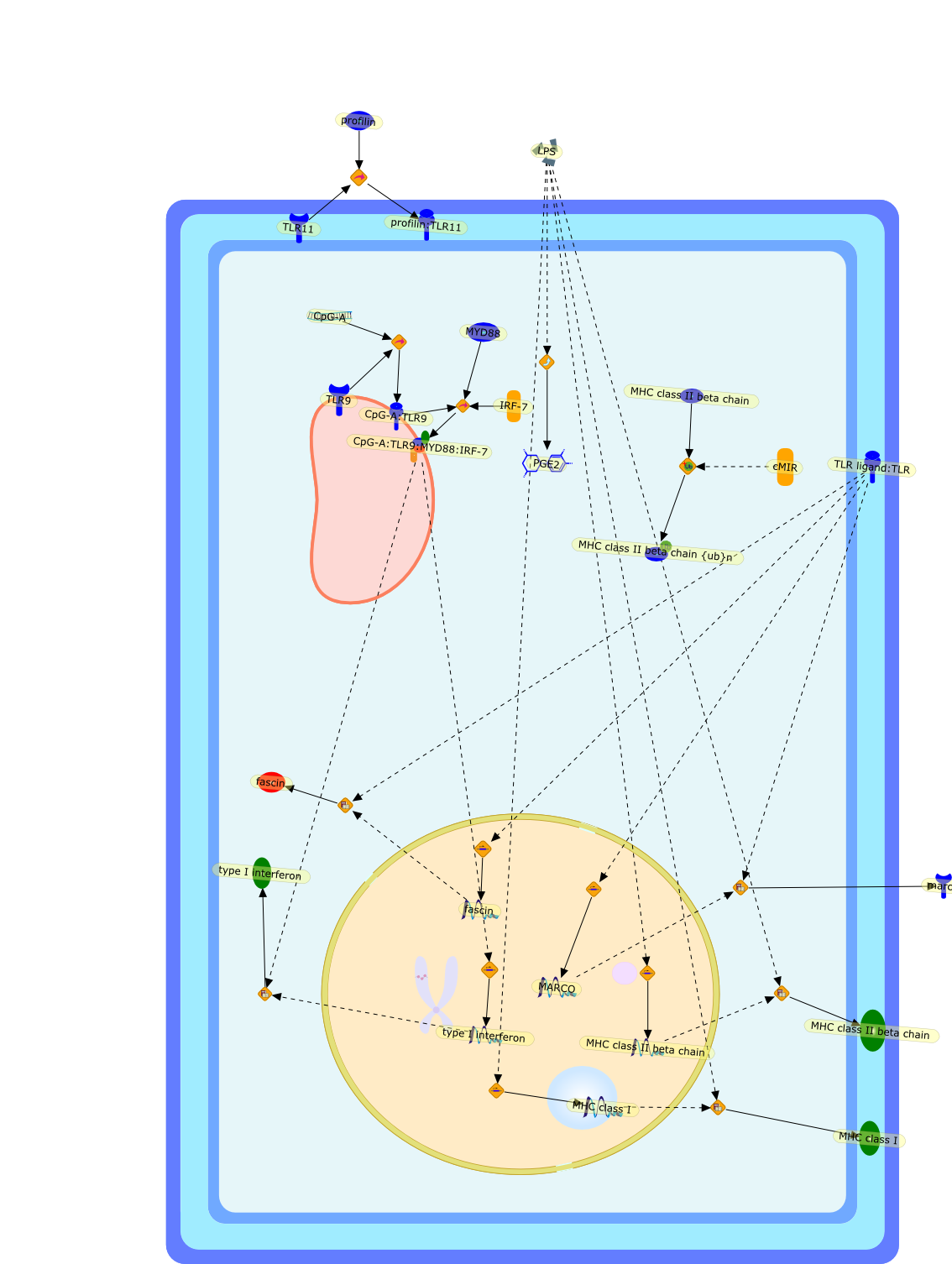
Proximal effects of Toll-like receptor activation in dendritic cells.
Affiliation
Division of Cell Biology and Immunology, College of Life Sciences, University ofDundee, Dundee DD1 5EH, United Kingdom. c.watts@dundee.ac.uk
Abstract
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signals induce dendritic cell (DC) differentiation andinfluence the immunological outcome of their interactions with T cells. Recentin vitro studies demonstrate that TLR signals also trigger strikingreorganisation of the DC vacuolar compartments, the cytoskeleton and themachinery of protein translation and turnover. Moreover, TLR ligation withinendosomes and phagosomes appears to establish organelle autonomous signals.These changes, which mostly occur within minutes to a few hours after TLRengagement, are adaptations relevant to the antigen capture, processing andmigratory phases of the DC life history.
PMID
17142025
|