| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
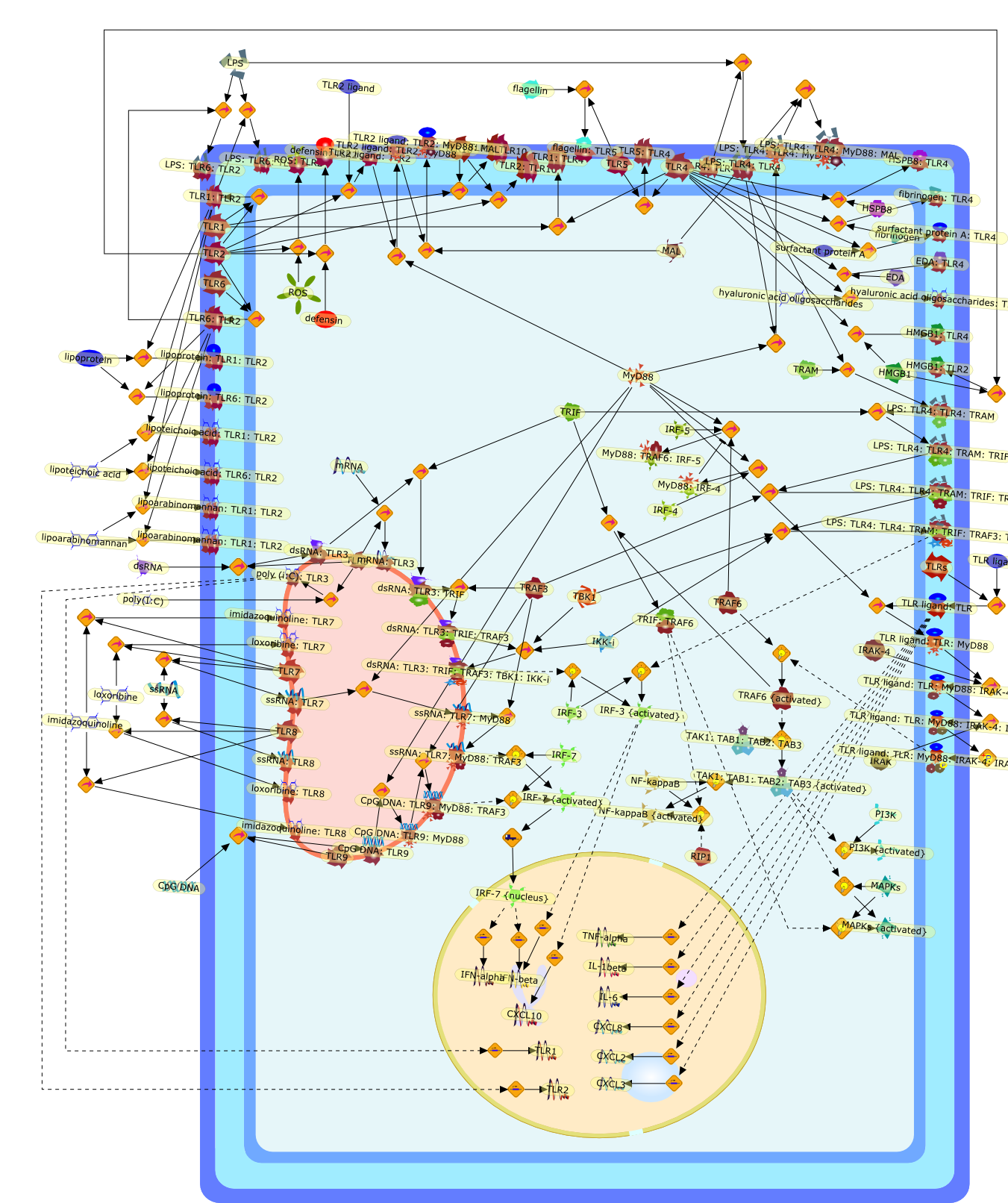
Translational mini-review series on Toll-like receptors: networks regulated byToll-like receptors mediate innate and adaptive immunity.
Affiliation
Academic Unit of Respiratory Medicine, School of Medicine and BiologicalSciences, University of Sheffield, UK.
Abstract
The Toll-like receptor (TLR) family provide key components of mammalian immunityand are part of the earliest surveillance mechanisms responding to infection.Their activation triggers the innate immune response, and is crucial to thesuccessful induction of Th1/Th2-phenotyped adaptive immunity. Innate immunitywas long considered to be non-specific and somewhat simple compared to adaptiveimmunity, mediated via the engulfment and lysis of microbial pathogens byphagocytic cells such as macrophages and neutrophils, and involving no complexprotein-protein interactions. The emergence of the TLR field has contributed toa revision of our understanding, and innate immunity is now viewed as a highlycomplex process, in line with adaptive immunity. This review will give a briefoverview of our current knowledge of TLR biology, and will focus on TLRs as keycomponents in complex networks that activate, integrate and select theappropriate innate and adaptive immune responses in the face of immunologicaldanger.
PMID
17223959
|