| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Therapeutic implications of the TLR and VDR partnership.
Affiliation
Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicineat University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA.
Abstract
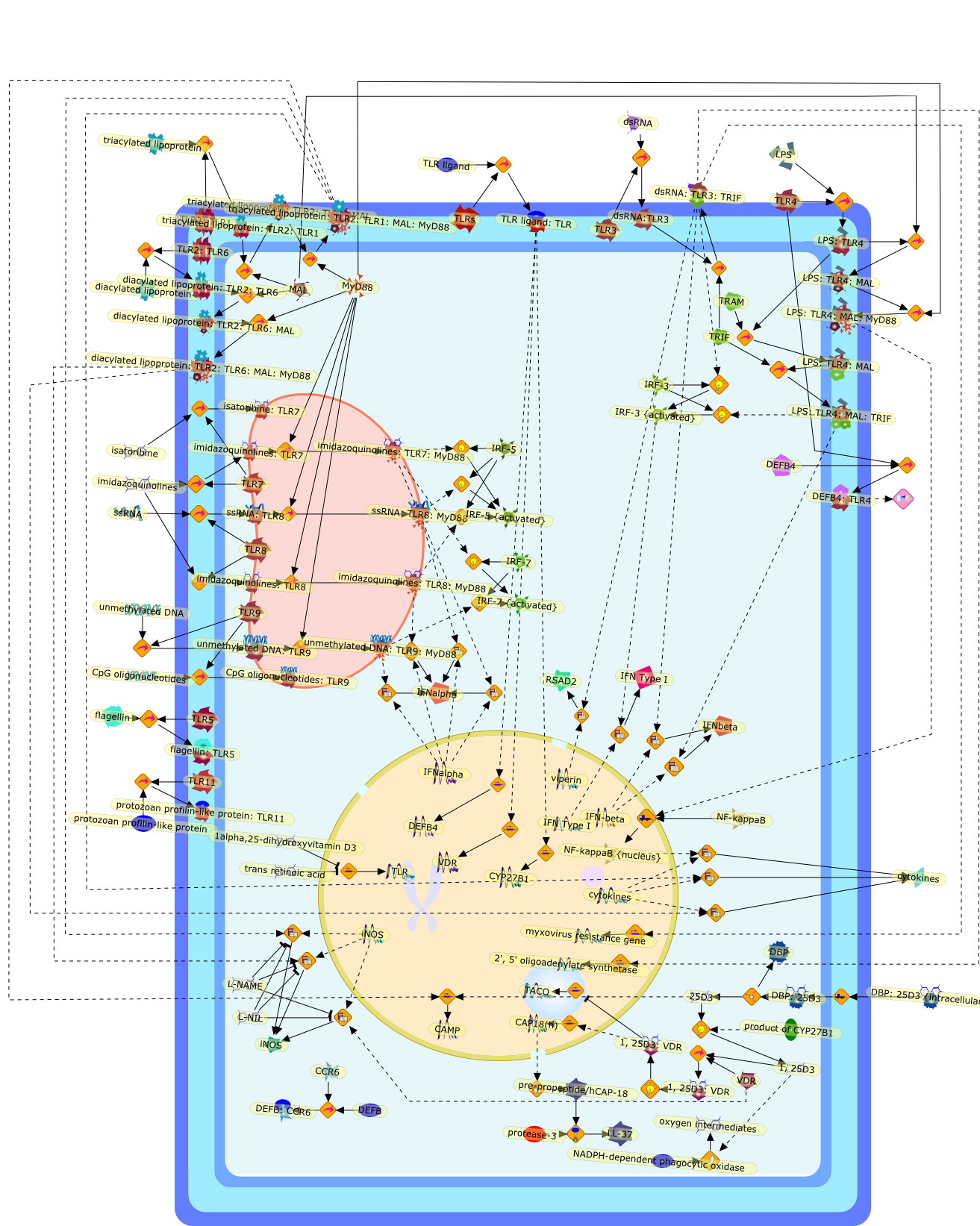
The innate immune system provides the host with an immediate and rapid defenseagainst invading microbes. Detection of foreign invaders is mediated by a classof receptors that are known as the pattern recognition receptors, such as thefamily of Toll-like receptors (TLRs). In humans, ten functional TLRs have beenidentified and they respond to conserved pathogen-associated molecular patternsderived from bacteria, mycoplasma, fungi and viruses. TLR activation leads todirect antimicrobial activity against both intracellular and extracellularbacteria, and induces an antiviral gene program. Recently, it was reported thatTLR2 activation leads to the use of vitamin D3 as a mechanism to combatMycobacterium tuberculosis. Here, we focus on recent findings concerning theTLR-induced antimicrobial mechanisms in humans and the therapeutic implicationsof these findings. Owing to their capability to combat a wide array ofpathogens, TLRs are attractive therapeutic targets. However, additionalknowledge about their antimicrobial mechanisms is needed.
PMID
17276732
|