| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
RIG-I: tri-ing to discriminate between self and non-self RNA.
Affiliation
School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2,Ireland.
Abstract
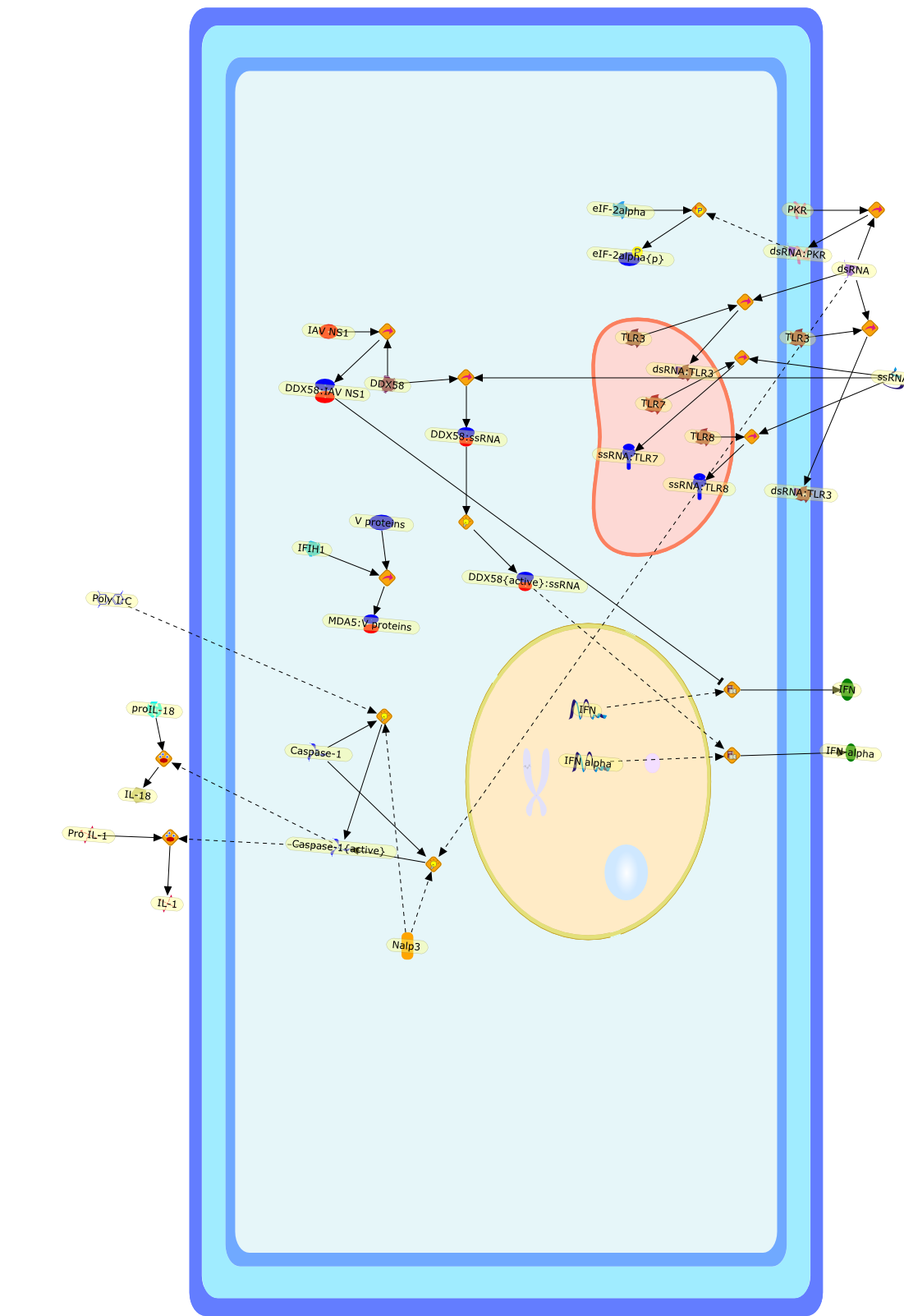
The ability to distinguish foreign nucleic acids from abundant self nucleicacids is essential to protect the host from invading pathogens. Several innateimmune surveillance systems have evolved to detect nucleic acids and triggercellular responses to eliminate foreign invaders. For RNA recognition, theseinclude double stranded (ds)RNA-dependent protein kinase, Toll-like receptor(TLR)3, TLR7, TLR8, retinoic acid-inducible gene (RIG)-I and melanomadifferentiation-associated gene 5. In the case of the nucleic-acid-sensing TLRs,endosomal localization is thought to be crucial for providing self versusnon-self discrimination. For RNA-sensing in the cytoplasm, RIG-I was recentlyshown to detect and directly bind to the 5'-end of certain viral RNA genomes,specifically, to a 5'-triphosphate group. Such 5'-triphosphates are generallyremoved from, or masked on, host RNA species, thereby remaining silent to innateimmunity and providing a structural basis for the distinction between self andnon-self RNA. The mechanisms by which MDA5 senses RNA are unclear at present butseem to involve the sensing of dsRNA structures.
PMID
17307033
|