| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
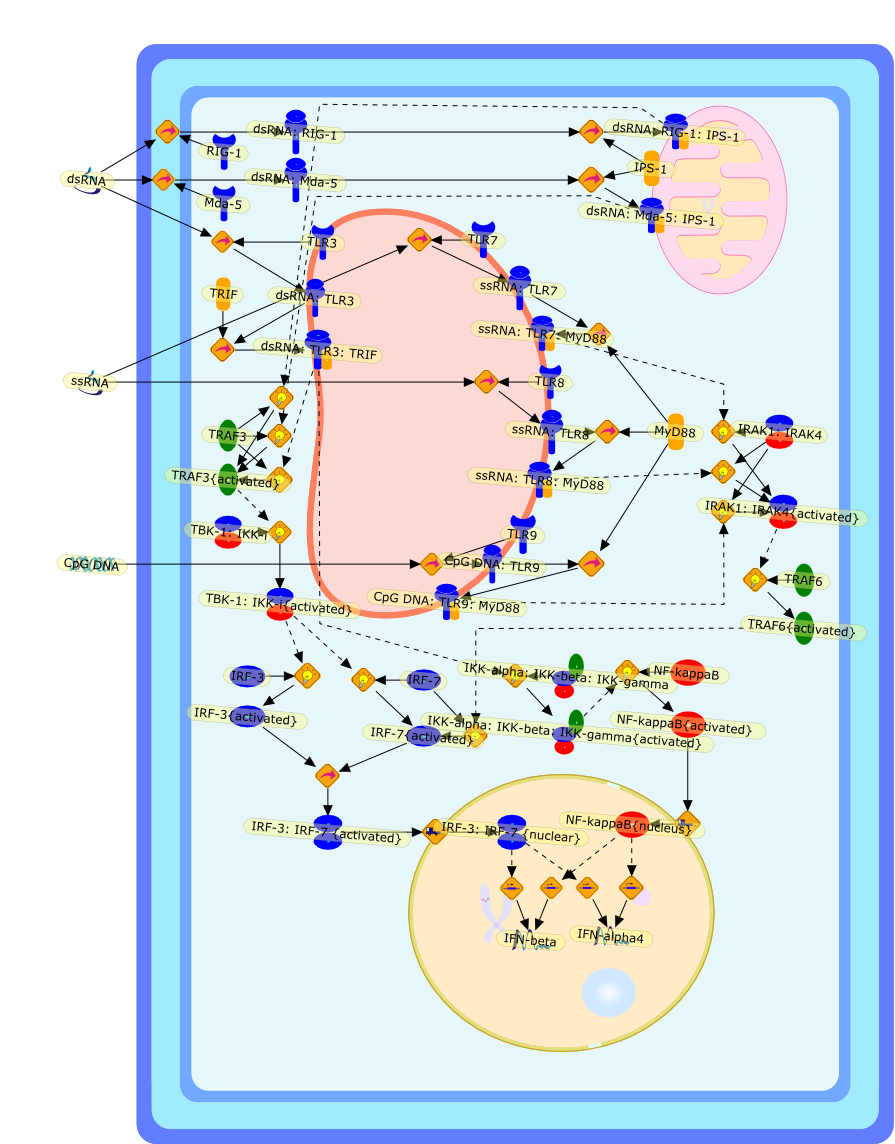
Innate immunity minireview series: making biochemical sense of nucleic acidsensors that trigger antiviral innate immunity.
Affiliation
Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology and theBiomolecular Sciences and Engineering Program, University of California, SantaBarbara, California 93106, USA. samuel@lifesci.ucsb.edu
Abstract
PMID
17395579
|