| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
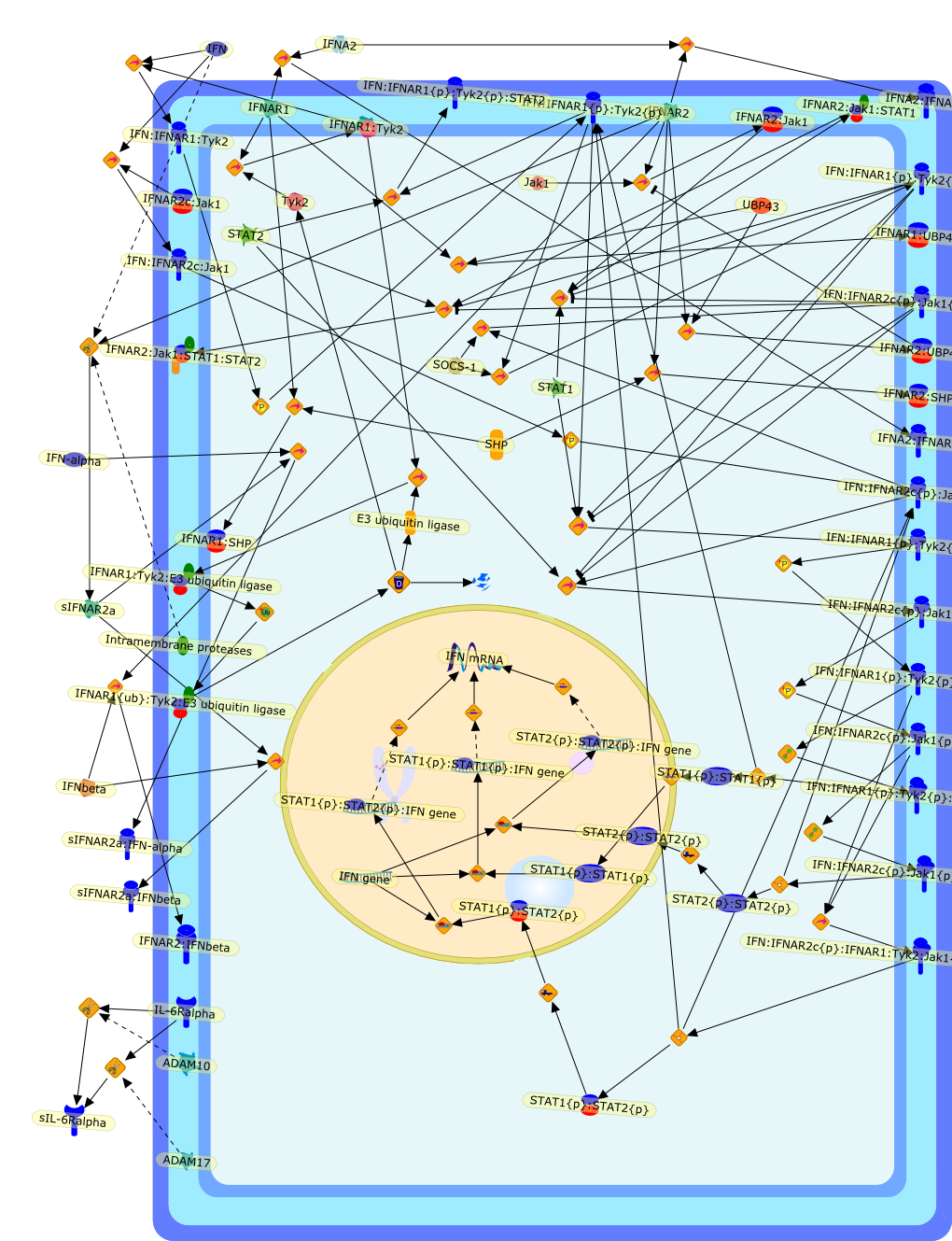
Type I interferon receptors: biochemistry and biological functions.
Affiliation
Centre for Functional Genomics and Human Disease, Monash Institute of MedicalResearch, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria 3168, Australia.
Abstract
PMID
17502368
|