| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
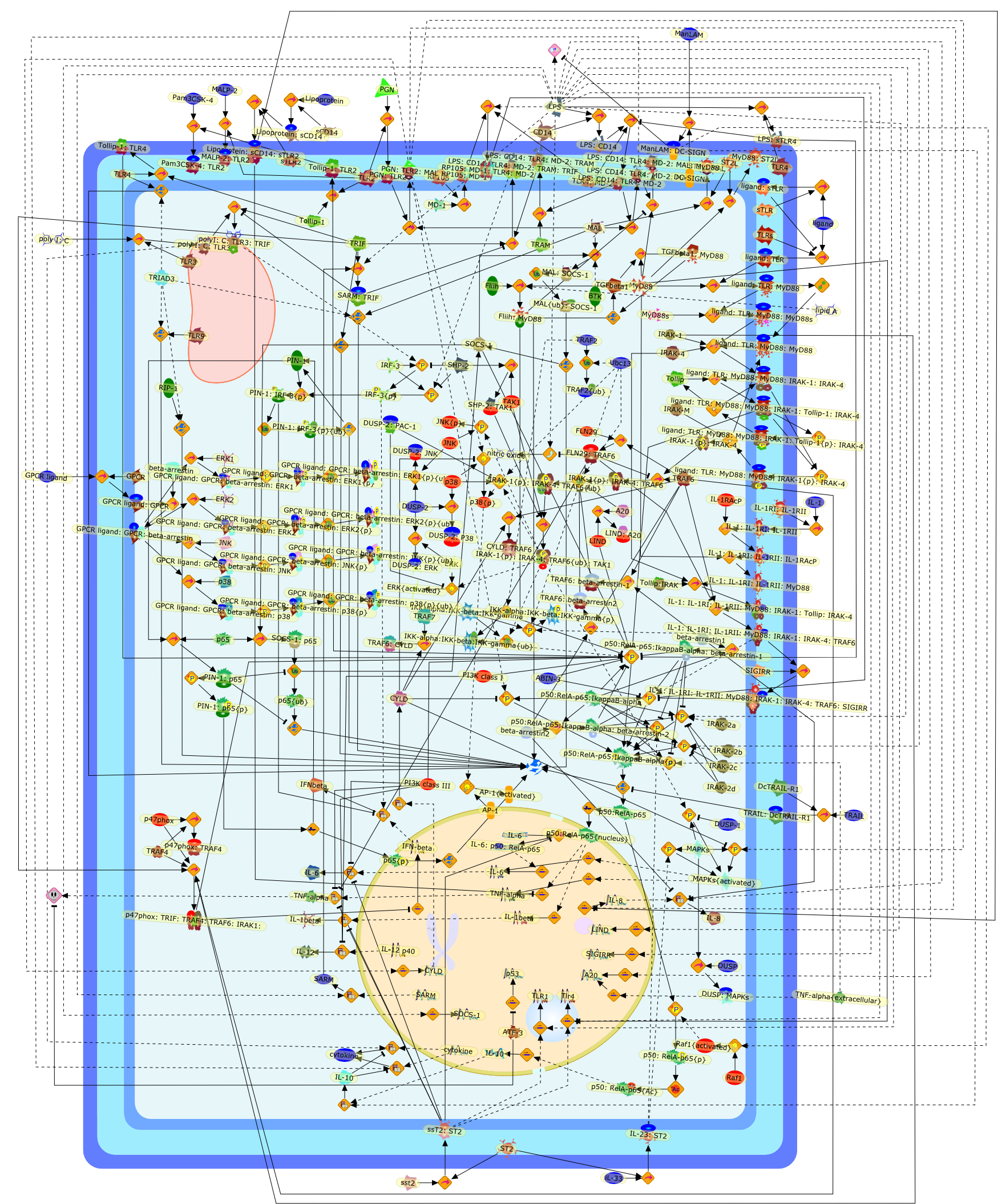
The negative regulation of Toll-like receptor and associated pathways.
Affiliation
Centre for Functional Genomics and Human Disease, Monash Institute of MedicalResearch, Monash University, Victoria, Australia.
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are essential mediators of both innate and adaptiveimmunity by recognizing and eliciting responses upon invasion of pathogens. Theresponse of TLRs must be stringently regulated as exaggerated expression ofsignalling components as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines can have devastatingeffects on the host, resulting in chronic inflammatory diseases, autoimmunedisorders and aid in the pathogenesis of TLR-associated human diseases.Therefore, it is essential that negative regulators act at multiple levelswithin TLR signalling cascades, as well as through eliciting negative-feedbackmechanisms in order to synchronize the positive activation and negativeregulation of signal transduction to avert potentially harmful immunologicalconsequences. This review explores the various mechanisms employed by negativeregulators to ensure the appropriate modulation of both immune and inflammatoryresponses.
PMID
17621314
|