| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
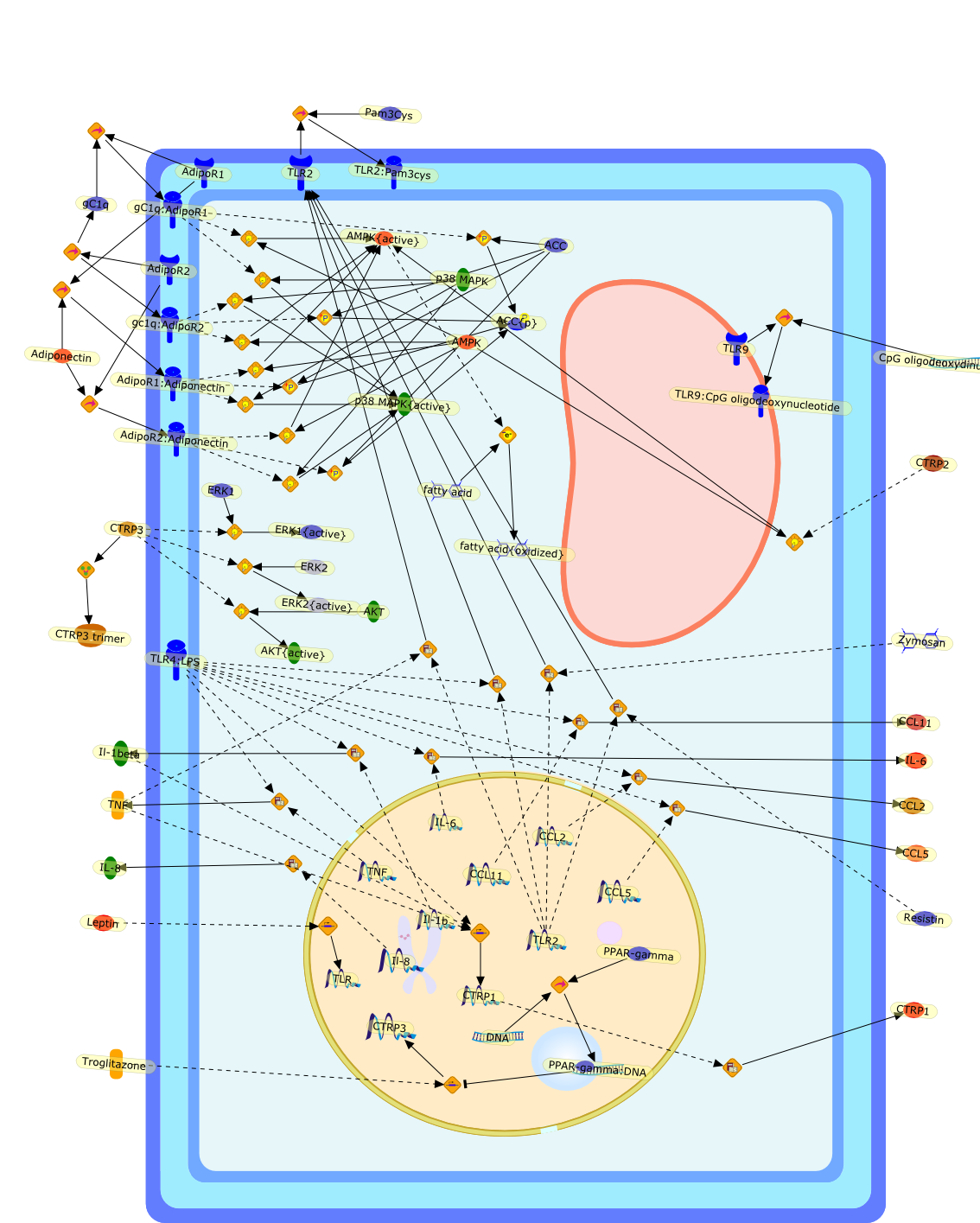
Adipose tissue as an immunological organ: Toll-like receptors, C1q/TNFs andCTRPs.
Affiliation
Department of Internal Medicine I, University of Regensburg, D-93042 Regensburg,Germany. andreas.schaeffler@klinik.uni-regensburg.de
Abstract
Adipose tissue has long been regarded as a mostly resting tissue that isdedicated solely to energy storage and release. However, in recent years, thisview has changed dramatically following new insights into the metabolic andimmunological functions of preadipocytes and adipocytes. There are several linesof evidence for the involvement of adipose tissue in innate and acquired immuneresponses. First, adipocytes are potent producers of proinflammatory cytokines,such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and chemokines.Furthermore, adipocytes secrete high amounts of adipokines, such as leptin,adiponectin and resistin, that regulate monocyte/macrophage function, and alsosecrete molecules associated with the innate immune system, such as theC1qTNF-related protein superfamily. Finally, preadipocytes and adipocytesexpress a broad spectrum of functional Toll-like receptors and the former canconvert into macrophage-like cells. Collectively, these data clearly establishthe role of adipose tissue as a new member of the immune system.
PMID
17681884
|