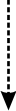| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll-like receptors: paving the path to T cell-driven autoimmunity?
Affiliation
Molecular Biomedicine, Institute of Integrative Biology, ETH Zurich, Wagistr 27,8952, Zurich, Switzerland.
Abstract
The development of autoimmunity is often associated with the presence ofpathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and signaling through toll-likereceptors (TLRs). Largely, the importance of PAMP-TLR ligation has beenattributed to inducing the maturation of antigen-presenting cells and productionof proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Recent evidence now shows thatPAMPs can activate effector and regulatory T cells revealing a further level ofcomplexity in the development of autoimmunity. TLR signaling on T cells acts asa form of costimulation, lowering the 'strength of signal' required forproliferation and survival. This apparent mechanism of immune homeostasis maybreak tolerance or anergy upon pathogen infection and promote the development ofimmune responses against self-antigens.
PMID
17888644
|