| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
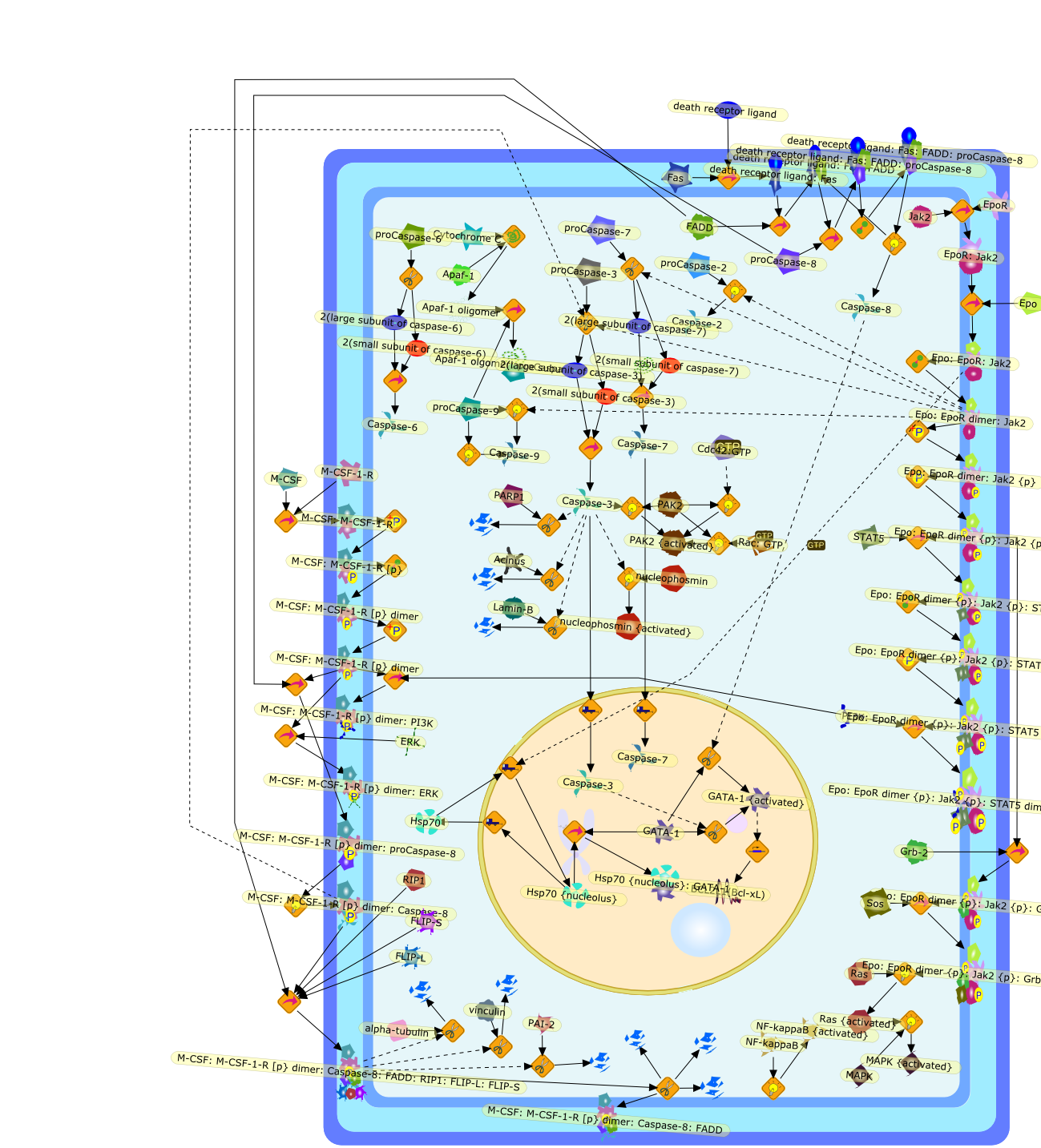
A role for caspases in the differentiation of erythroid cells and macrophages.
Affiliation
INSERM, UMR 866, F-21079 Dijon, France.
Abstract
Several cysteine proteases of the caspase family play a central role in manyforms of cell death by apoptosis. Other enzymes of the family are involved incytokine maturation along inflammatory response. In recent years, severalcaspases involved in cell death were shown to play a role in other cellularprocesses such as proliferation and differentiation. In the present review, wesummarize the current knowledge of the role of caspases in the differentiationof erythroid cells and macrophages. Based on these two examples, we show thatthe nature of involved enzymes, the pathways leading to their activation inresponse to specific growth factors, and the specificity of the target proteinsthat are cleaved by the activated enzymes strongly differ from one cell type toanother. Deregulation of these pathways is thought to play a role in thepathophysiology of low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes, characterized byexcessive activation of caspases and erythroid precursor apoptosis, and that ofchronic myelomonocytic leukemia, characterized by a defective activation ofcaspases in monocytes exposed to M-CSF, which blocks their differentiation.
PMID
17905508
|