| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Toll like receptors and autoimmunity: a critical appraisal.
Affiliation
Department of Internal Medicine and Division of Rheumatology, Immunology andAllergy, University of Crete, Medical School, Voutes 71500, Heraklion, Greece.
Abstract
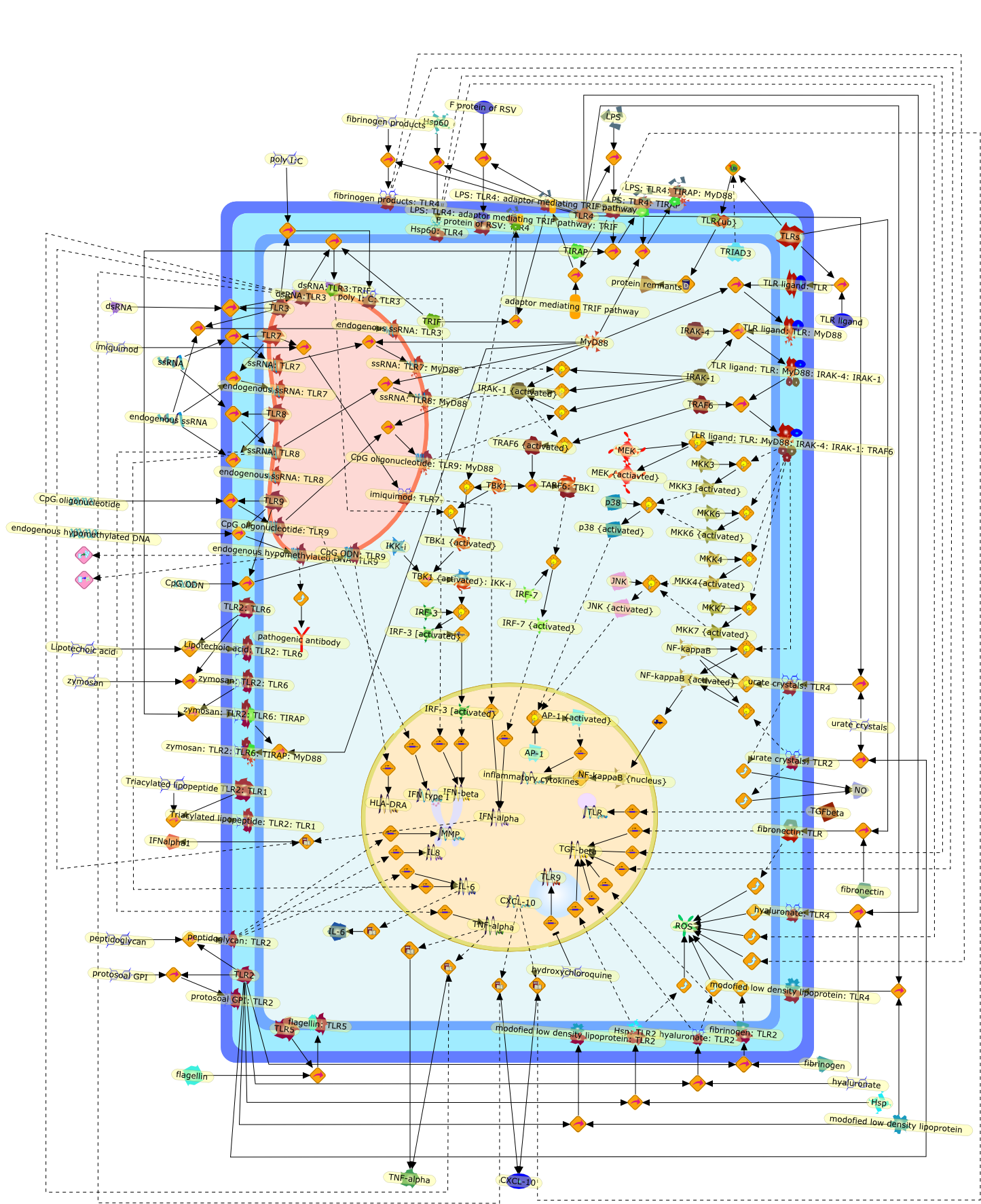
There is a constant interplay between the innate and adaptive immune systems,which leads to a protective immune response against pathogens and contributeseffectively to self-non-self discrimination. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are keycomponents of the innate immune system, which activate multiple inflammatorypathways and coordinate systemic defense against pathogens. In addition torecognizing unique molecular patterns associated with different classes ofpathogens, TLRs may also recognize a number of self proteins and endogenousnucleic acids. Data originating predominantly from animal models of autoimmunedisease and circumstantial data from human patients suggest that inappropriateactivation of TLR pathways by endogenous or exogenous ligands may lead to theinitiation and/or perpetuation of autoimmune responses and tissue injury.
PMID
17959357
|