| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Intracellular NOD-like receptors in host defense and disease.
Affiliation
Department of Pathology and Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of MichiganMedical School, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA.
Abstract
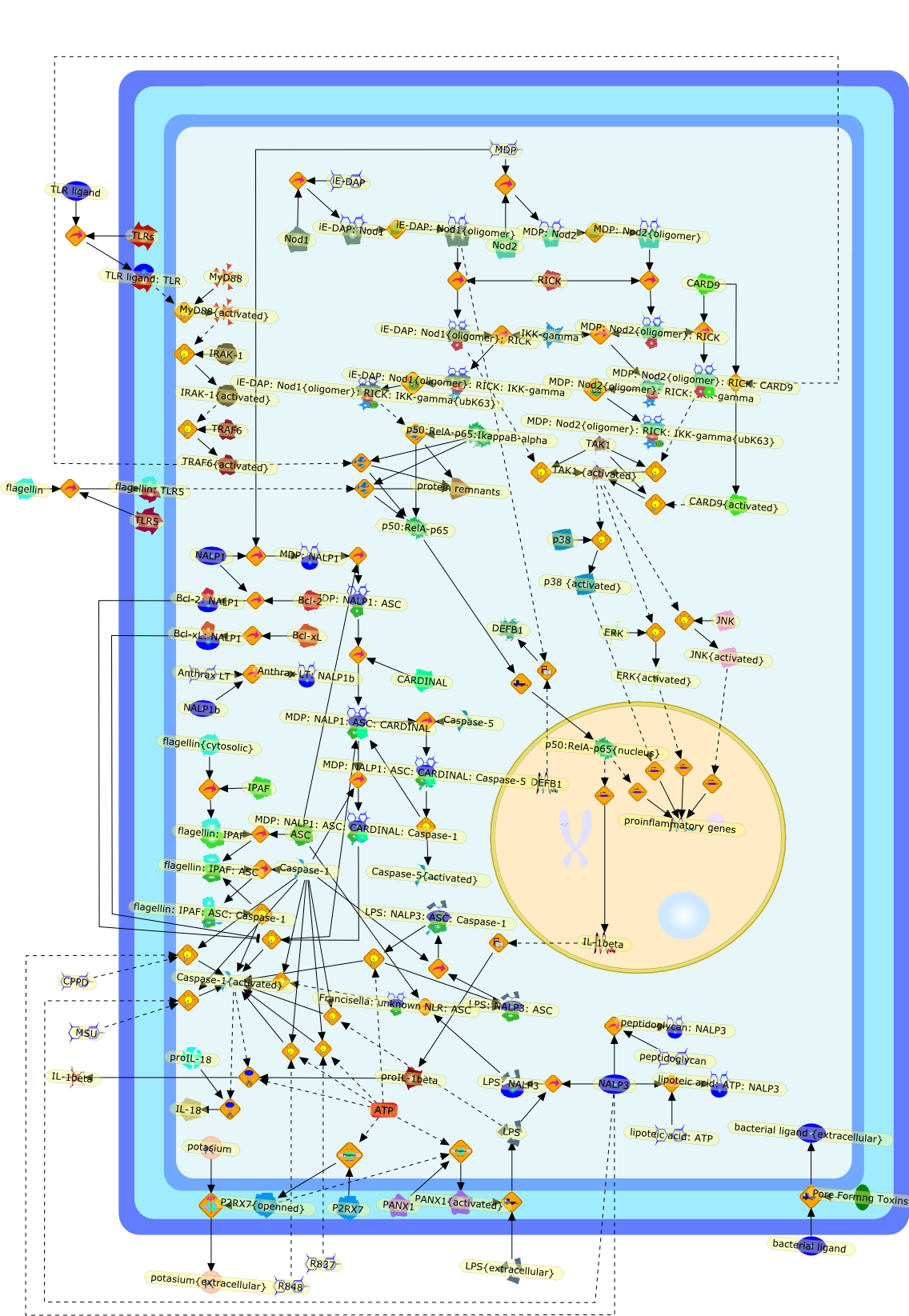
The innate immune system comprises several classes of pattern recognitionreceptors, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs), NOD-like receptors (NLRs), andRIG-1-like receptors (RLRs). TLRs recognize microbes on the cell surface and inendosomes, whereas NLRs and RLRs detect microbial components in the cytosol.Here we discuss the recent understanding in NLRs. Two NLRs, NOD1 and NOD2, sensethe cytosolic presence of the peptidoglycan fragments meso-DAP and muramyldipeptide, respectively, and drive the activation of mitogen-activated proteinkinase (MAPK) and the transcription factor NF-kappaB. A different set of NLRsinduces caspase-1 activation through the assembly of large protein complexesnamed inflammasomes. Genetic variations in several NLR members are associatedwith the development of inflammatory disorders. Further understanding of NLRsshould provide new insights into the mechanisms of host defense and thepathogenesis of inflammatory diseases.
PMID
17967410
|