| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Anti-inflammatory actions of PPAR ligands: new insights on cellular andmolecular mechanisms.
Affiliation
Biomedical Sciences Division, University of California, Riverside, Riverside, CA92521-0121, USA. daniel.straus@ucr.edu
Abstract
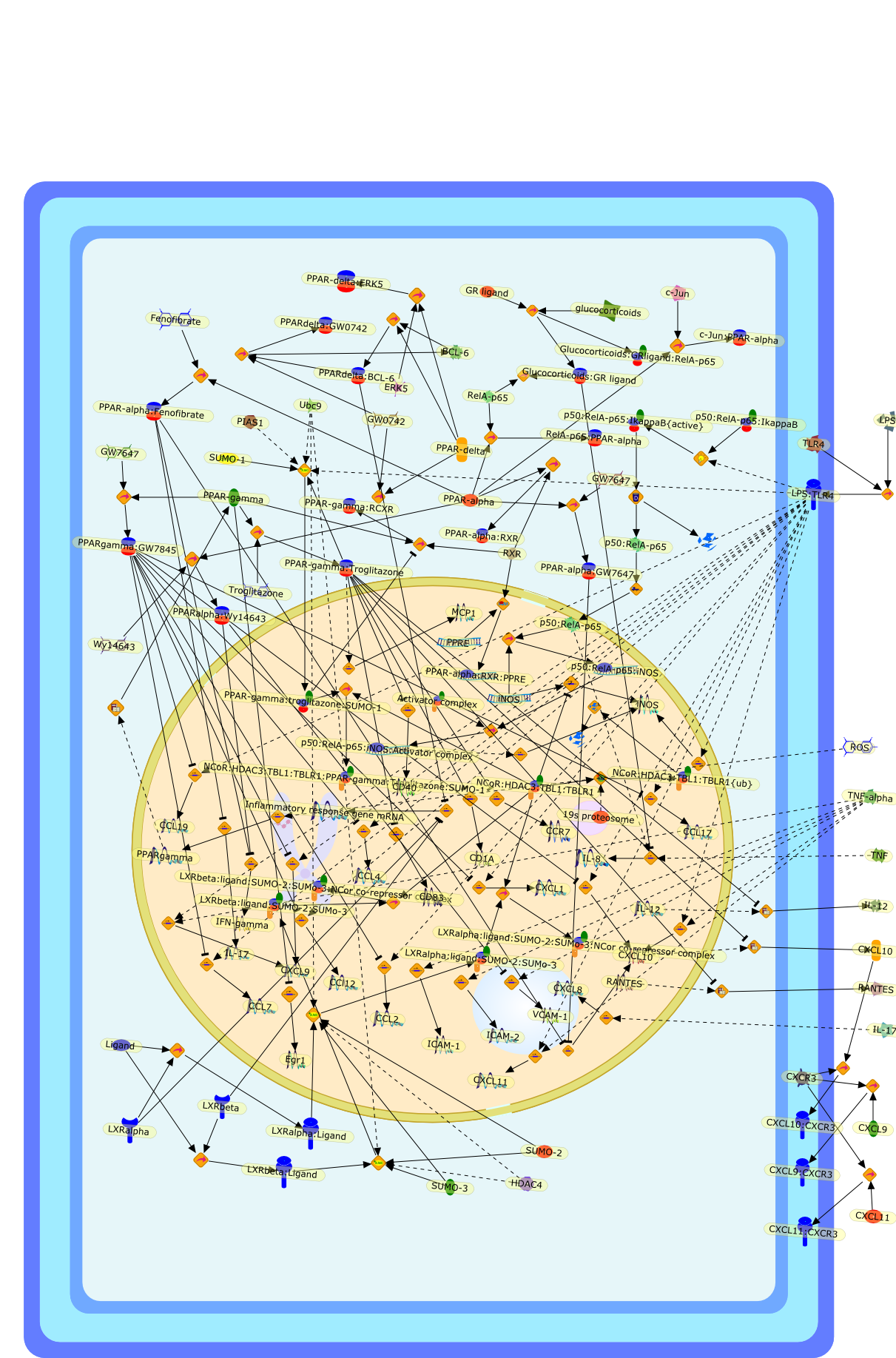
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARalpha, -gamma, and-beta/delta) are nuclear receptors with distinct patterns of expression in manycell types both within and outside the immune system. PPAR ligands haveanti-inflammatory activity in a variety of mouse models for acute and chronicinflammation. In macrophages, PPARgamma ligands repress expression of a subsetof Toll-like receptor (TLR) target genes by a molecular mechanism termedligand-dependent transrepression. In chronic inflammation, ligand-boundPPARalpha represses production of IFNgamma and IL-17 by CD4(+) T cells, andPPARgamma ligands modulate dendritic cell function to elicit the development ofanergic CD4(+) T cells. PPAR ligands also repress expression of cell adhesionmolecules on endothelial cells and the secretion of chemokines by epithelial andother cells, decreasing the recruitment of leukocytes to the site ofinflammation. The anti-inflammatory activity of PPAR ligands in mouse modelssuggests their possible use for treating human inflammatory and autoimmunediseases.
PMID
17981503
|