| Original Literature | Model OverView |
|---|---|
|
Publication
Title
Nod1 and Nod2 in innate immunity and human inflammatory disorders.
Affiliation
Department of Immunology, Medical Sciences Building, University of Toronto, 1King's College Circle, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 1A8.
Abstract
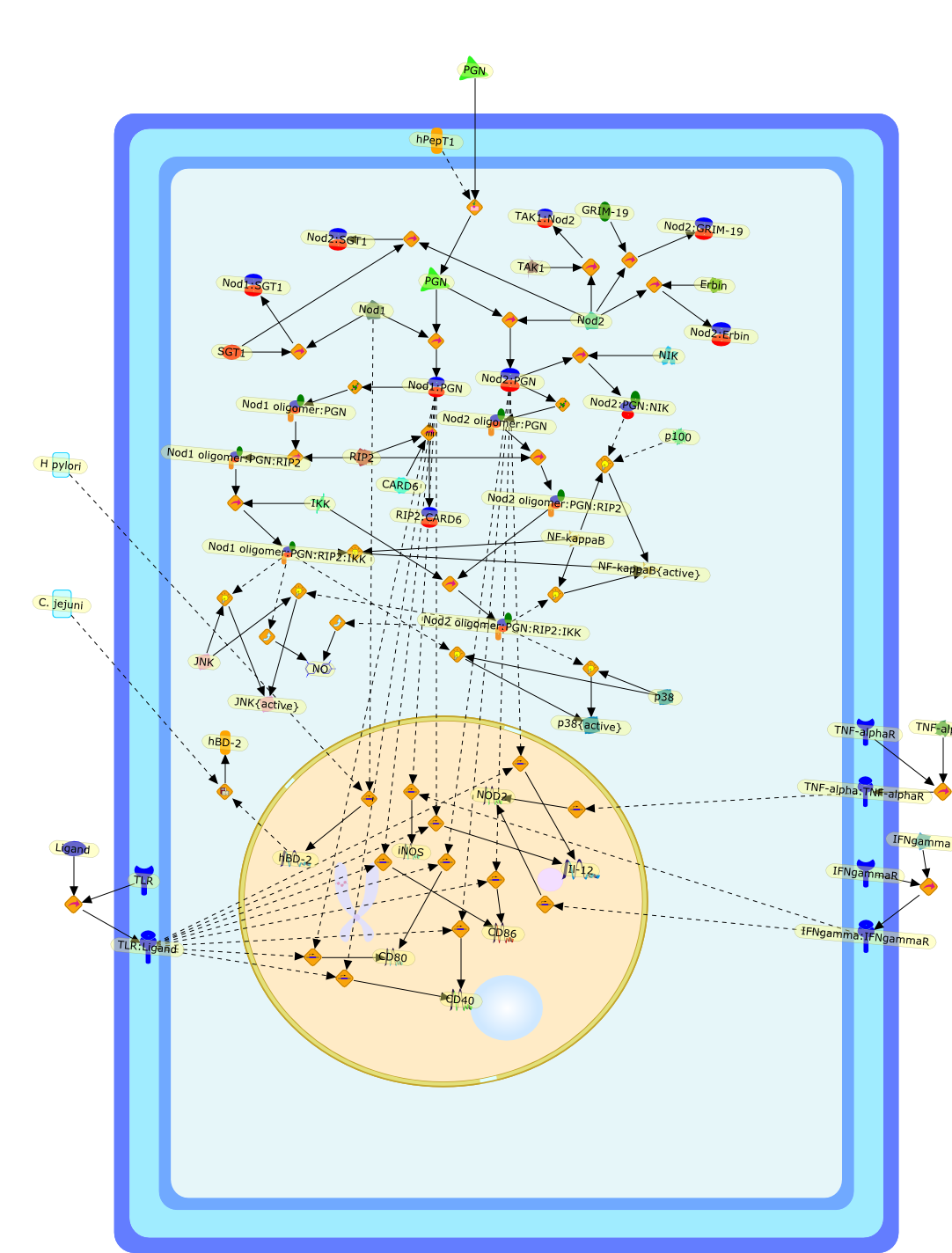
Nod (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain) 1 and Nod2 are intracellularPRMs (pattern-recognition molecules) of the NLR (Nod-like receptor) family.These proteins are implicated in the detection of bacterial peptidoglycan andregulate pro-inflammatory pathways in response to bacteria by inducingsignalling pathways such as NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) and MAPKs(mitogen-activated protein kinases). The Nod proteins act independently of theTLR (Toll-like receptor) cascade, but potently synergize with the latter totrigger innate immune responses to microbes. Most importantly, mutations in Nod2have been shown to confer susceptibility to several chronic inflammatorydisorders, including Crohn's disease, Blau syndrome and early-onset sarcoidosis,underscoring the role of Nod2 in inflammatory homoeostasis. This reviewsummarizes the most recent findings in the field of Nod1 and Nod2 research.
PMID
18031249
|